Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation
- PMID: 29191830
- PMCID: PMC5961061
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.TM117.000259
Lipoic acid metabolism and mitochondrial redox regulation
Abstract
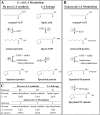
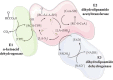
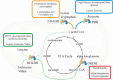
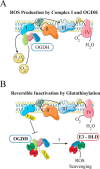
Lipoic acid is an essential cofactor for mitochondrial metabolism and is synthesized de novo using intermediates from mitochondrial fatty-acid synthesis type II, S-adenosylmethionine and iron-sulfur clusters. This cofactor is required for catalysis by multiple mitochondrial 2-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes, including pyruvate dehydrogenase, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase. Lipoic acid also plays a critical role in stabilizing and regulating these multienzyme complexes. Many of these dehydrogenases are regulated by reactive oxygen species, mediated through the disulfide bond of the prosthetic lipoyl moiety. Collectively, its functions explain why lipoic acid is required for cell growth, mitochondrial activity, and coordination of fuel metabolism.
Keywords: cell metabolism; lipoic acid; mitochondria; oxidation-reduction (redox); redox regulation; tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) (Krebs cycle).
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
A hub for regulation of mitochondrial metabolism: Fatty acid and lipoic acid biosynthesis.IUBMB Life. 2024 Jun;76(6):332-344. doi: 10.1002/iub.2802. Epub 2023 Dec 13. IUBMB Life. 2024. PMID: 38088214 Review.
-
Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014 Jul;37(4):553-63. doi: 10.1007/s10545-014-9705-8. Epub 2014 Apr 29. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. PMID: 24777537 Review.
-
Differential diagnosis of lipoic acid synthesis defects.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016 Nov;39(6):781-793. doi: 10.1007/s10545-016-9975-4. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2016. PMID: 27586888 Review.
-
Dynamic Relay of Protein-Bound Lipoic Acid in Staphylococcus aureus.J Bacteriol. 2019 Oct 21;201(22):e00446-19. doi: 10.1128/JB.00446-19. Print 2019 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 31451544 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the lipoyltransferase LIPT1 gene cause a fatal disease associated with a specific lipoylation defect of the 2-ketoacid dehydrogenase complexes.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Apr 1;23(7):1907-15. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt585. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24256811
Cited by
-
Targeting cuproptosis by zinc pyrithione in triple-negative breast cancer.iScience. 2023 Oct 16;26(11):108218. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108218. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37953954 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the role of Cuproptosis genes and their related long non-coding RNA in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: a comprehensive bioinformatics study.BMC Cancer. 2022 Nov 6;22(1):1141. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10278-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36335291 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Peptide-Lipoic Acid Cationic Polymers with Redox Responsiveness and Low Toxicity for Gene Delivery.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 5;9(3):3499-3506. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07194. eCollection 2024 Jan 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38284089 Free PMC article.
-
A Trypanosoma brucei ORFeome-Based Gain-of-Function Library Identifies Genes That Promote Survival during Melarsoprol Treatment.mSphere. 2020 Oct 7;5(5):e00769-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00769-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 33028684 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Lipoic Acid and Its Enantiomers Prevent Methemoglobin Formation and DNA Damage Induced by Dapsone Hydroxylamine: Molecular Mechanism and Antioxidant Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):57. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010057. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reed L. J. (2006) in Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, pp. 319–347, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ
-
- Patterson E. L., Brockman J. A. Jr., Day F. P., Pierce J. V., Macchi M. E., Hoffman C. E., Fong C. T., Stokstad E. L., and Jukes T. H. (1951) Crystallization of a derivative of protogen-B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 73, 5919–5920 10.1021/ja01156a566 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

