Cardiac myocyte miR-29 promotes pathological remodeling of the heart by activating Wnt signaling
- PMID: 29158499
- PMCID: PMC5696364
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01737-4
Cardiac myocyte miR-29 promotes pathological remodeling of the heart by activating Wnt signaling
Abstract
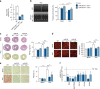
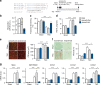
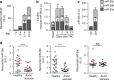
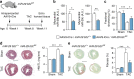
Chronic cardiac stress induces pathologic hypertrophy and fibrosis of the myocardium. The microRNA-29 (miR-29) family has been found to prevent excess collagen expression in various organs, particularly through its function in fibroblasts. Here, we show that miR-29 promotes pathologic hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes and overall cardiac dysfunction. In a mouse model of cardiac pressure overload, global genetic deletion of miR-29 or antimiR-29 infusion prevents cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis and improves cardiac function. Targeted deletion of miR-29 in cardiac myocytes in vivo also prevents cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, indicating that the function of miR-29 in cardiac myocytes dominates over that in non-myocyte cell types. Mechanistically, we found cardiac myocyte miR-29 to de-repress Wnt signaling by directly targeting four pathway factors. Our data suggests that, cell- or tissue-specific antimiR-29 delivery may have therapeutic value for pathological cardiac remodeling and fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-22 regulates cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling in response to stress.Circ Res. 2013 Apr 26;112(9):1234-43. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300682. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23524588 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-378 suppresses myocardial fibrosis through a paracrine mechanism at the early stage of cardiac hypertrophy following mechanical stress.Theranostics. 2018 Apr 3;8(9):2565-2582. doi: 10.7150/thno.22878. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29721099 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic cardiac-targeted delivery of miR-1 reverses pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy and attenuates pathological remodeling.J Am Heart Assoc. 2013 Apr 23;2(2):e000078. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.113.000078. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013. PMID: 23612897 Free PMC article.
-
HSF1 deficiency accelerates the transition from pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy to heart failure through endothelial miR-195a-3p-mediated impairment of cardiac angiogenesis.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018 May;118:193-207. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2018.03.017. Epub 2018 Apr 5. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29626503
-
[Research progress on miR-21 in heart diseases].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019 Apr 25;48(2):214-218. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2019.04.14. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2019. PMID: 31309761 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Current Status of MicroRNAs that Target the Wnt Signaling Pathway in Regulation of Osteogenesis and Bone Metabolism: A Review.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Apr 8;27:e929510. doi: 10.12659/MSM.929510. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 33828067 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-29b-3p alleviates coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury via regulating BMF and GSK-3β.Apoptosis. 2023 Feb;28(1-2):210-221. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01788-z. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Apoptosis. 2023. PMID: 36315357
-
Right Ventricle and Epigenetics: A Systematic Review.Cells. 2023 Nov 23;12(23):2693. doi: 10.3390/cells12232693. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Editing Therapeutics: Advances, Challenges and Perspectives on Combating Heart Disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023 Apr;37(2):401-411. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07391-3. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023. PMID: 36239832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-29c-tetrahedral framework nucleic acids: Towards osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and bone regeneration in critical-sized calvarial defects.Cell Prolif. 2024 Jul;57(7):e13624. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13624. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Cell Prolif. 2024. PMID: 38414296 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

