Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy
- PMID: 29147025
- PMCID: PMC5818153
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc.2017.96
Sphingolipid metabolism in cancer signalling and therapy
Abstract
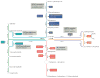
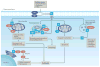
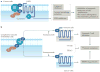
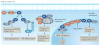
Sphingolipids, including the two central bioactive lipids ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), have opposing roles in regulating cancer cell death and survival, respectively, and there have been exciting developments in understanding how sphingolipid metabolism and signalling regulate these processes in response to anticancer therapy. Recent studies have provided mechanistic details of the roles of sphingolipids and their downstream targets in the regulation of tumour growth and response to chemotherapy, radiotherapy and/or immunotherapy using innovative molecular, genetic and pharmacological tools to target sphingolipid signalling nodes in cancer cells. For example, structure-function-based studies have provided innovative opportunities to develop mechanism-based anticancer therapeutic strategies to restore anti-proliferative ceramide signalling and/or inhibit pro-survival S1P-S1P receptor (S1PR) signalling. This Review summarizes how ceramide-induced cellular stress mediates cancer cell death through various mechanisms involving the induction of apoptosis, necroptosis and/or mitophagy. Moreover, the metabolism of ceramide for S1P biosynthesis, which is mediated by sphingosine kinase 1 and 2, and its role in influencing cancer cell growth, drug resistance and tumour metastasis through S1PR-dependent or receptor-independent signalling are highlighted. Finally, studies targeting enzymes involved in sphingolipid metabolism and/or signalling and their clinical implications for improving cancer therapeutics are also presented.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sphingolipids and cancer: ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in the regulation of cell death and drug resistance.Future Oncol. 2010 Oct;6(10):1603-24. doi: 10.2217/fon.10.116. Future Oncol. 2010. PMID: 21062159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer treatment strategies targeting sphingolipid metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;688:185-205. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-6741-1_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20919655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Sphingolipid Mediators on the Determination of Cochlear Survival in Ototoxicity.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018;11(4):279-284. doi: 10.2174/1874467211666180516101111. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29766830 Review.
-
Sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling in cancer therapeutics and drug resistance.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(216):3-27. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1511-4_1. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23563649 Review.
-
The control of the balance between ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate by sphingosine kinase: oxidative stress and the seesaw of cell survival and death.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;163(1):26-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 May 18. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22613819 Review.
Cited by
-
Sorting-free metabolic profiling uncovers the vulnerability of fatty acid β-oxidation in in vitro quiescence models.Mol Syst Biol. 2022 Sep;18(9):e10716. doi: 10.15252/msb.202110716. Mol Syst Biol. 2022. PMID: 36094015 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics of newborn dried blood spots reveals sex-specific associations with pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.Leuk Res. 2021 Jul;106:106585. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106585. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Leuk Res. 2021. PMID: 33971561 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrahigh resolution lipid mass spectrometry imaging of high-grade serous ovarian cancer mouse models.Front Chem. 2024 Jan 8;11:1332816. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1332816. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38260043 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in lipidomics may be potential biomarkers for early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer.Acta Cir Bras. 2020 Jul 6;35(5):e202000508. doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020200050000008. Acta Cir Bras. 2020. PMID: 32638847 Free PMC article.
-
Pilot Multi-Omic Analysis of Human Bile from Benign and Malignant Biliary Strictures: A Machine-Learning Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 21;12(6):1644. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061644. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:139–150. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Bell RM. Lysosphingolipids inhibit protein kinase C: implications for the sphingolipidoses. Science. 1987;235:670–674. - PubMed
-
- Dressler KA, Mathias S, Kolesnick RN. Tumor necrosis factor-α activates the sphingomyelin signal transduction pathway in a cell-free system. Science. 1992;255:1715–1718. - PubMed
-
- Ogretmen B, Hannun YA. Biologically active sphingolipids in cancer pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:604–616. - PubMed
-
- Cuvillier O, et al. Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature. 1996;381:800–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

