Genome sequence of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus
- PMID: 29136191
- PMCID: PMC5740986
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/gix109
Genome sequence of the small brown planthopper, Laodelphax striatellus
Abstract
Background: Laodelphax striatellus Fallén (Hemiptera: Delphacidae) is one of the most destructive rice pests. L. striatellus is different from 2 other rice planthoppers with a released genome sequence, Sogatella furcifera and Nilaparvata lugens, in many biological characteristics, such as host range, dispersal capacity, and vectoring plant viruses. Deciphering the genome of L. striatellus will further the understanding of the genetic basis of the biological differences among the 3 rice planthoppers.
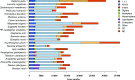
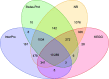
Findings: A total of 190 Gb of Illumina data and 32.4 Gb of Pacbio data were generated and used to assemble a high-quality L. striatellus genome sequence, which is 541 Mb in length and has a contig N50 of 118 Kb and a scaffold N50 of 1.08 Mb. Annotated repetitive elements account for 25.7% of the genome. A total of 17 736 protein-coding genes were annotated, capturing 97.6% and 98% of the BUSCO eukaryote and arthropoda genes, respectively. Compared with N. lugens and S. furcifera, L. striatellus has the smallest genome and the lowest gene number. Gene family expansion and transcriptomic analyses provided hints to the genomic basis of the differences in important traits such as host range, migratory habit, and plant virus transmission between L. striatellus and the other 2 planthoppers.
Conclusions: We report a high-quality genome assembly of L. striatellus, which is an important genomic resource not only for the study of the biology of L. striatellus and its interactions with plant hosts and plant viruses, but also for comparison with other planthoppers.
Keywords: annotation; comparative genomics; genome sequencing; insects; virus transmission.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chromosomal-level genomes of three rice planthoppers provide new insights into sex chromosome evolution.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 Jan;21(1):226-237. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13242. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021. PMID: 32780934
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of the Wnt Gene Family in Three Rice Planthoppers: Sogatella furcifera, Laodelphax striatellus, and Nilaparvata lugens.J Insect Sci. 2022 Sep 1;22(5):2. doi: 10.1093/jisesa/ieac049. J Insect Sci. 2022. PMID: 36082678 Free PMC article.
-
The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) and a comparative mitogenomic analysis of three predominant rice planthoppers.Gene. 2014 Jan 1;533(1):100-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.117. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24120898
-
The small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus) as a vector of the rice stripe virus.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023 Feb;112(2):e21992. doi: 10.1002/arch.21992. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36575628 Review.
-
Bacterial reproductive manipulators in rice planthoppers.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019 Jun;101(2):e21548. doi: 10.1002/arch.21548. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30912174 Review.
Cited by
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Insects.Animals (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;11(4):1118. doi: 10.3390/ani11041118. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-quality genome of the zoophytophagous stink bug, Nesidiocoris tenuis, informs their food habit adaptation.G3 (Bethesda). 2024 Feb 7;14(2):jkad289. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad289. G3 (Bethesda). 2024. PMID: 38113473 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Transcriptional Responses of Interactions between Insect Vectors and Plant Viruses.Cells. 2022 Feb 16;11(4):693. doi: 10.3390/cells11040693. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35203347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Diversity and Functional Complementation of Alimentary Canal Microbiota Ensure Small Brown Planthopper to Adapt Different Biogeographic Environments.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 17;10:2953. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02953. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010074 Free PMC article.
-
The grasshopper genome reveals long-term gene content conservation of the X Chromosome and temporal variation in X Chromosome evolution.Genome Res. 2024 Aug 20;34(7):997-1007. doi: 10.1101/gr.278794.123. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 39103228 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dmitriev DA. 3I Interactive Keys and Taxonomic Databases.2003. http://dmitriev.speciesfile.org/index.asp. Accessed 1 May 2017.
-
- Genus Laodelphax Fennah, 1963. College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Delaware; http://ag.udel.edu/research/delphacid/species/Laodelphax.htm. Accessed 1 May 2017.
-
- Sun DZ, Jiang L. Research on the inheritance and breeding of rice stripe resistance. Chin Agricult Sci Bull 2006;12:073.
-
- Huang H, Xue J, Zhuo J et al. . Comparative analysis of the transcriptional responses to low and high temperatures in three rice planthopper species. Mol Ecol 2017;26(10):2726–37. - PubMed
-
- Zhou G, Wen J, Cai D et al. . Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus: a new proposed Fijivirus species in the family Reoviridae. Chin Sci Bull 2008;53(23):3677–85.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

