Experimental asthma persists in IL-33 receptor knockout mice because of the emergence of thymic stromal lymphopoietin-driven IL-9+ and IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid cell subpopulations
- PMID: 29132961
- PMCID: PMC5945345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.10.020
Experimental asthma persists in IL-33 receptor knockout mice because of the emergence of thymic stromal lymphopoietin-driven IL-9+ and IL-13+ type 2 innate lymphoid cell subpopulations
Abstract
Background: IL-33 plays an important role in the development of experimental asthma.
Objective: We sought to study the role of the IL-33 receptor suppressor of tumorigenicity 2 (ST2) in the persistence of asthma in a mouse model.
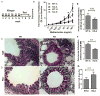
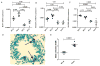
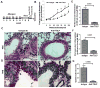
Methods: We studied allergen-induced experimental asthma in ST2 knockout (KO) and wild-type control mice. We measured airway hyperresponsiveness by using flexiVent; inflammatory indices by using ELISA, histology, and real-time PCR; and type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s) in lung single-cell preparations by using flow cytometry.
Results: Airway hyperresponsiveness was increased in allergen-treated ST2 KO mice and comparable with that in allergen-treated wild-type control mice. Peribronchial and perivascular inflammation and mucus production were largely similar in both groups. Persistence of experimental asthma in ST2 KO mice was associated with an increase in levels of thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-9, and IL-13, but not IL-5, in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Expectedly, ST2 deletion caused a reduction in IL-13+ CD4 T cells, forkhead box P3-positive regulatory T cells, and IL-5+ ILC2s. Unexpectedly, ST2 deletion led to an overall increase in innate lymphoid cells (CD45+lin-CD25+ cells) and IL-13+ ILC2s, emergence of a TSLP receptor-positive IL-9+ ILC2 population, and an increase in intraepithelial mast cell numbers in the lung. An anti-TSLP antibody abrogated airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and mucus production in allergen-treated ST2 KO mice. It also caused a reduction in innate lymphoid cell, ILC2, and IL-9+ and IL-13+ ILC2 numbers in the lung.
Conclusions: Genetic deletion of the IL-33 receptor paradoxically increases TSLP production, which stimulates the emergence of IL-9+ and IL-13+ ILC2s and mast cells and leads to development of chronic experimental asthma. An anti-TSLP antibody abrogates all pathologic features of asthma in this model.
Keywords: Asthma; IL-33 receptor; IL-9; mast cells; thymic stromal lymphopoietin; type 2 innate lymphoid cells.
Copyright © 2017 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

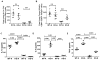

Similar articles
-
Respiratory syncytial virus infection activates IL-13-producing group 2 innate lymphoid cells through thymic stromal lymphopoietin.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Sep;138(3):814-824.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.01.050. Epub 2016 Apr 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27156176 Free PMC article.
-
The interleukin-33 receptor ST2 is important for the development of peripheral airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a house dust mite mouse model of asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2016 Mar;46(3):479-90. doi: 10.1111/cea.12683. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016. PMID: 26609909
-
The Innate Cytokines IL-25, IL-33, and TSLP Cooperate in the Induction of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Expansion and Mucous Metaplasia in Rhinovirus-Infected Immature Mice.J Immunol. 2017 Aug 15;199(4):1308-1318. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700216. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28701507 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and Regulation of Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Receptor Heterocomplex in the Innate-Adaptive Immunity of Pediatric Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Apr 18;19(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041231. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29670037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s): The spotlight in asthma pathogenesis and lung tissue injury.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021 Mar 1;49(2):208-216. doi: 10.15586/aei.v49i2.29. eCollection 2021. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2021. PMID: 33641310 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 1 Receptor-Like 1 (IL1RL1) Promotes Airway Bacterial and Viral Infection and Inflammation.Infect Immun. 2019 Jun 20;87(7):e00340-19. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00340-19. Print 2019 Jul. Infect Immun. 2019. PMID: 31061143 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-(1-7) suppresses airway inflammation and airway remodeling via inhibiting ATG5 in allergic asthma.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Nov 2;23(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02719-7. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37919667 Free PMC article.
-
Anisakis pegreffii Extract Induces Airway Inflammation with Airway Remodeling in a Murine Model System.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Sep 17;2021:2522305. doi: 10.1155/2021/2522305. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34580637 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB1 inhibits memory formation and supports effector function of ILC2s in memory-driven asthma.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 27;14:1217776. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1217776. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37575259 Free PMC article.
-
T cells and ILC2s are major effector cells in influenza-induced exacerbation of allergic airway inflammation in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2019 Jan;49(1):144-156. doi: 10.1002/eji.201747421. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Eur J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 29762870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morita H, Moro K, Koyasu S. Innate lymphoid cells in allergic and nonallergic inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;138:1253–1264. - PubMed
-
- Klose CS, Artis D. Innate lymphoid cells as regulators of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:765–74. - PubMed
-
- Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2007;179:2551–5. - PubMed
-
- Endo Y, Hirahara K, Iinuma T, Shinoda K, Tumes DJ, Asou HK, et al. The interleukin-33-p38 kinase axis confers memory T helper 2 cell pathogenicity in the airway. Immunity. 2015;42:294–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

