Determining the contents and cell origins of apoptotic bodies by flow cytometry
- PMID: 29089562
- PMCID: PMC5663759
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-14305-z
Determining the contents and cell origins of apoptotic bodies by flow cytometry
Abstract
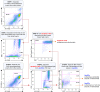
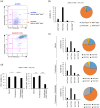
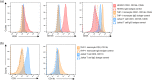
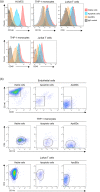
Over 200 billion cells undergo apoptosis every day in the human body in order to maintain tissue homeostasis. Increased apoptosis can also occur under pathological conditions including infection and autoimmune disease. During apoptosis, cells can fragment into subcellular membrane-bound vesicles known as apoptotic bodies (ApoBDs). We recently developed a flow cytometry-based method to accurately differentiate ApoBDs from other particles (e.g. cells and debris). In the present study, we aim to further characterize subsets of ApoBDs based on intracellular contents and cell type-specific surface markers. Utilizing a flow cytometry-based approach, we demonstrated that intracellular contents including nuclear materials and mitochondria are distributed to some, but not all ApoBDs. Interestingly, the mechanism of ApoBD formation could affect the distribution of intracellular contents into ApoBDs. Furthermore, we also showed that ApoBDs share the same surface markers as their cell of origin, which can be used to distinguish cell type-specific ApoBDs from a mixed culture. These studies demonstrate that ApoBDs are not homogeneous and can be divided into specific subclasses based on intracellular contents and cell surface markers. The described flow cytometry-based method to study ApoBDs could be used in future studies to better understand the function of ApoBDs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Detection and Isolation of Apoptotic Bodies to High Purity.J Vis Exp. 2018 Aug 12;(138):58317. doi: 10.3791/58317. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 30148494 Free PMC article.
-
Pannexin-1 channel regulates nuclear content packaging into apoptotic bodies and their size.Proteomics. 2021 Jul;21(13-14):e2000097. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000097. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33661579
-
Apoptotic Bodies: Mechanism of Formation, Isolation and Functional Relevance.Subcell Biochem. 2021;97:61-88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-67171-6_4. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33779914
-
Apoptotic bodies: bioactive treasure left behind by the dying cells with robust diagnostic and therapeutic application potentials.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Jul 12;21(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01969-1. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37434199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the Therapeutic Effects of Apoptotic Bodies on Systemic Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 26;23(15):8202. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158202. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cell-free microRNAs as Non-invasive Diagnostic and Prognostic Bio- markers in Pancreatic Cancer.Curr Genomics. 2019 Dec;20(8):569-580. doi: 10.2174/1389202921666191217095017. Curr Genomics. 2019. PMID: 32581645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic Bodies in the Pancreatic Tumor Cell Culture Media Enable Label-Free Drug Sensitivity Assessment by Impedance Cytometry.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021 Aug;5(8):e2100438. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202100438. Epub 2021 May 20. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34015194 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Opportunities and Challenges.Front Oncol. 2022 May 25;12:884369. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.884369. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35692794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moving beyond size and phosphatidylserine exposure: evidence for a diversity of apoptotic cell-derived extracellular vesicles in vitro.J Extracell Vesicles. 2019 Apr 26;8(1):1608786. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2019.1608786. eCollection 2019. J Extracell Vesicles. 2019. PMID: 31069027 Free PMC article.
-
Horizontal Gene Transfer: From Evolutionary Flexibility to Disease Progression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 19;8:229. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00229. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32509768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

