NOX4-dependent neuronal autotoxicity and BBB breakdown explain the superior sensitivity of the brain to ischemic damage
- PMID: 29087944
- PMCID: PMC5699031
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1705034114
NOX4-dependent neuronal autotoxicity and BBB breakdown explain the superior sensitivity of the brain to ischemic damage
Abstract
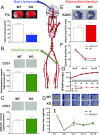
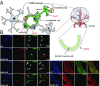
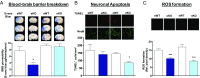
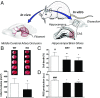
Ischemic injury represents the most frequent cause of death and disability, and it remains unclear why, of all body organs, the brain is most sensitive to hypoxia. In many tissues, type 4 NADPH oxidase is induced upon ischemia or hypoxia, converting oxygen to reactive oxygen species. Here, we show in mouse models of ischemia in the heart, brain, and hindlimb that only in the brain does NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) lead to ischemic damage. We explain this distinct cellular distribution pattern through cell-specific knockouts. Endothelial NOX4 breaks down the BBB, while neuronal NOX4 leads to neuronal autotoxicity. Vascular smooth muscle NOX4, the common denominator of ischemia within all ischemic organs, played no apparent role. The direct neuroprotective potential of pharmacological NOX4 inhibition was confirmed in an ex vivo model, free of vascular and BBB components. Our results demonstrate that the heightened sensitivity of the brain to ischemic damage is due to an organ-specific role of NOX4 in blood-brain-barrier endothelial cells and neurons. This mechanism is conserved in at least two rodents and humans, making NOX4 a prime target for a first-in-class mechanism-based, cytoprotective therapy in the unmet high medical need indication of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: BBB; NOX4; endothelium; neurotoxicity; stroke.
Copyright © 2017 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Foxo1-induced miR-92b down-regulation promotes blood-brain barrier damage after ischaemic stroke by targeting NOX4.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jun;25(11):5269-5282. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16537. Epub 2021 May 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33955666 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of NOX4 by betulinic acid protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017 Oct;37(5):744-749. doi: 10.1007/s11596-017-1798-5. Epub 2017 Oct 20. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 29058289
-
Blood brain barrier-targeted lipid nanoparticles improved the neuroprotection of Ferrostatin-1 against cerebral ischemic damage in an experimental stroke model.Exp Neurol. 2024 Sep;379:114849. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114849. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38857748
-
Potential benefits and harms of NADPH oxidase type 4 in the kidneys and cardiovascular system.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019 Apr 1;34(4):567-576. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy161. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. PMID: 29931336 Review.
-
NADPH Oxidase-Related Pathophysiology in Experimental Models of Stroke.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 11;18(10):2123. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102123. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29019942 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Novel Therapeutics Targeting the Blood-Brain Barrier: From Barrier to Carrier.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Aug;8(16):e2101090. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101090. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34085418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOX2 and NOX5 are increased in cardiac microvascular endothelium of deceased COVID-19 patients.Int J Cardiol. 2023 Jan 1;370:454-462. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2022.10.172. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Int J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 36332749 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular Biology of Superoxide-Generating NADPH Oxidase 5-Implications in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019 Mar 1;30(7):1027-1040. doi: 10.1089/ars.2018.7583. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2019. PMID: 30334629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotective Effect of SCM-198 through Stabilizing Endothelial Cell Function.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 11;2019:7850154. doi: 10.1155/2019/7850154. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827699 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress in the Brain: Basic Concepts and Treatment Strategies in Stroke.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;10(12):1886. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121886. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

