TAMeless traitors: macrophages in cancer progression and metastasis
- PMID: 29065107
- PMCID: PMC5729447
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.356
TAMeless traitors: macrophages in cancer progression and metastasis
Abstract
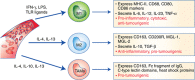
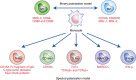
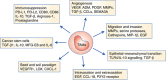
Macrophages are conventionally classified into M1 and M2 subtypes according to their differentiation status and functional role in the immune system. However, accumulating evidence suggests that this binary classification system is insufficient to account for the remarkable plasticity of macrophages that gives rise to an immense diversity of subtypes. This diverse spectrum of macrophage subtypes play critical roles in various homeostatic and immune functions, but remain far from being fully characterised. In addition to their roles in normal physiological conditions, macrophages also play crucial roles in disease conditions such as cancer. In this review, we discuss the roles tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) play in regulating different steps of tumour progression and metastasis, and the opportunities to target them in the quest for cancer prevention and treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor-associated macrophages: role in cancer development and therapeutic implications.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019 Oct;42(5):591-608. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00453-z. Epub 2019 May 29. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2019. PMID: 31144271 Review.
-
Redirecting tumor-associated macrophages to become tumoricidal effectors as a novel strategy for cancer therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 18;8(29):48436-48452. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17061. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28467800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor versus tumor-associated macrophages: how hot is the link?Integr Cancer Ther. 2008 Jun;7(2):90-5. doi: 10.1177/1534735408319060. Integr Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18550889 Review.
-
The roles of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.Cell Immunol. 2020 Jul;353:104119. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104119. Epub 2020 May 4. Cell Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32446032 Review.
-
Tumor associated macrophages and neutrophils in tumor progression.J Cell Physiol. 2013 Jul;228(7):1404-12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24260. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23065796 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Potential Therapeutic Targets and Immune Cell Infiltration Characteristics in Osteosarcoma Using Bioinformatics Strategy.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 21;10:1628. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01628. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32974202 Free PMC article.
-
A Structurally Simple Vaccine Candidate Reduces Progression and Dissemination of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101250. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101250. Epub 2020 Jun 6. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32629615 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles remodel tumor environment for cancer immunotherapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Dec 13;22(1):203. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01898-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38087360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic host immunity and PD-L1/PD-1 blockade efficacy: developments after "IFN-γ from lymphocytes induces PD-L1 expression and promotes progression of ovarian cancer".Br J Cancer. 2023 Feb;128(3):461-467. doi: 10.1038/s41416-022-01960-x. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36068276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cuproptosis-associated ncRNAs predict breast cancer subtypes.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 26;19(2):e0299138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299138. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38408075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baghel KS, Tewari BN, Shrivastava R, Malik SA, Lone MU, Jain NK, Tripathi C, Kanchan RK, Dixit S, Singh K, Mitra K, Negi MP, Srivastava M, Misra S, Bhatt ML, Bhadauria S (2016) Macrophages promote matrix protrusive and invasive function of breast cancer cells via MIP-1beta dependent upregulation of MYO3A gene in breast cancer cells. Oncoimmunology 5(7): e1196299. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F (2004) Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer 4(7): 540–550. - PubMed
-
- Campbell MJ, Tonlaar NY, Garwood ER, Huo D, Moore DH, Khramtsov AI, Au A, Baehner F, Chen Y, Malaka DO, Lin A, Adeyanju OO, Li S, Gong C, McGrath M, Olopade OI, Esserman LJ (2011) Proliferating macrophages associated with high grade, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and poor clinical outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128(3): 703–711. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casazza A, Laoui D, Wenes M, Rizzolio S, Bassani N, Mambretti M, Deschoemaeker S, Van Ginderachter JA, Tamagnone L, Mazzone M (2013) Impeding macrophage entry into hypoxic tumor areas by Sema3A/Nrp1 signaling blockade inhibits angiogenesis and restores antitumor immunity. Cancer Cell 24(6): 695–709. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

