Regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptors by Ubiquilin1
- PMID: 29054976
- PMCID: PMC5842694
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20170620
Regulation of insulin-like growth factor receptors by Ubiquilin1
Abstract
Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates growth, proliferation and survival. Dysregulation of IGF pathway contributes to the initiation, progression and metastasis of cancer and is also involved in diseases of glucose metabolism, such as diabetes. We have identified Ubiquilin1 (UBQLN1) as a novel interaction partner of IGF1R, IGF2R and insulin receptor (INSR). UBQLN family of proteins have been studied primarily in the context of protein quality control and in the field of neurodegenerative disorders. Our laboratory discovered a link between UBQLN1 function and tumorigenesis, such that UBQLN1 is lost and underexpressed in 50% of human lung adenocarcinoma cases. We demonstrate here that UBQLN1 regulates the expression and activity of IGF1R. Following loss of UBQLN1 in lung adenocarcinoma cells, there is accelerated loss of IGF1R. Despite decreased levels of total receptors, the ratio of active : total receptors is higher in cells that lack UBQLN1. UBQLN1 also regulates INSR and IGF2R post-stimulation with ligand. We conclude that UBQLN1 is essential for normal regulation of IGF receptors. UBQLN-1-deficient cells demonstrate increased cell viability compared with control when serum-starved and stimulation of IGF pathway in these cells increased their migratory potential by 3-fold. As the IGF pathway is involved in processes of normal growth, development, metabolism and cancer progression, understanding its regulation by Ubiquilin1 can be of tremendous value to many disciplines.
Keywords: Ubiquilin; insulin-like growth factor; receptor tyrosine kinases; trafficking; turnover.
© 2017 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

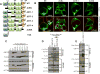
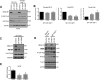
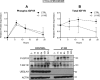
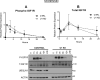
Similar articles
-
Ubiquilin proteins regulate EGFR levels and activity in lung adenocarcinoma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;122(1):43-52. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29830. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32720736 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquilin1 represses migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human non-small cell lung cancer cells.Oncogene. 2015 Mar 26;34(13):1709-17. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.97. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24747970 Free PMC article.
-
The STI and UBA Domains of UBQLN1 Are Critical Determinants of Substrate Interaction and Proteostasis.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Aug;118(8):2261-2270. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25880. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28075048 Free PMC article.
-
Minireview: nuclear insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors: a novel paradigm in signal transduction.Endocrinology. 2013 May;154(5):1672-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-2165. Epub 2013 Mar 18. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23507573 Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor ligands, receptors, and binding proteins in cancer.J Pathol. 2005 Jan;205(2):145-53. doi: 10.1002/path.1712. J Pathol. 2005. PMID: 15641016 Review.
Cited by
-
UBR-box containing protein, UBR5, is over-expressed in human lung adenocarcinoma and is a potential therapeutic target.BMC Cancer. 2020 Aug 31;20(1):824. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07322-1. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32867711 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormally elevated ubiquilin‑1 expression in breast cancer regulates metastasis and stemness via AKT signaling.Oncol Rep. 2021 Nov;46(5):236. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8187. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34528694 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquilin 2 modulates ALS/FTD-linked FUS-RNA complex dynamics and stress granule formation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Dec 4;115(49):E11485-E11494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811997115. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30442662 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquilin proteins regulate EGFR levels and activity in lung adenocarcinoma cells.J Cell Biochem. 2021 Jan;122(1):43-52. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29830. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 32720736 Free PMC article.
-
UBQLN Family Members Regulate MYC in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;15(13):3389. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133389. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yarden Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. European journal of cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 4):S3–8. - PubMed
-
- Renehan AG, O'Connell J, O'Halloran D, Shanahan F, Potten CS, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM. Acromegaly and colorectal cancer: a comprehensive review of epidemiology, biological mechanisms, and clinical implications. Horm Metab Res. 2003;35:712–725. - PubMed
-
- Laron Z. The GH-IGF1 axis and longevity. The paradigm of IGF1 deficiency. Hormones (Athens) 2008;7:24–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

