Dietary resveratrol confers apoptotic resistance to oxidative stress in myoblasts
- PMID: 29053994
- PMCID: PMC5694367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.08.008
Dietary resveratrol confers apoptotic resistance to oxidative stress in myoblasts
Abstract
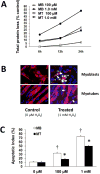
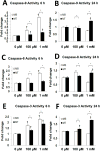
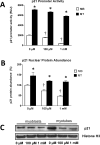
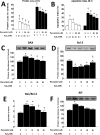
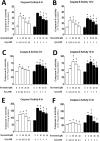
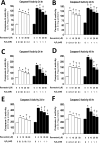
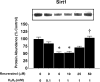
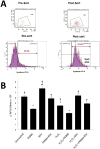
High levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contribute to muscle cell death in aging and disuse. We have previously found that resveratrol can reduce oxidative stress in response to aging and hindlimb unloading in rodents in vivo, but it was not known if resveratrol would protect muscle stem cells during repair or regeneration when oxidative stress is high. To test the protective role of resveratrol on muscle stem cells directly, we treated the C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line with moderate (100 μM) or very high (1 mM) levels of H2O2 in the presence or absence of resveratrol. The p21 promoter activity declined in myoblasts in response to high ROS, and this was accompanied a greater nuclear to cytoplasmic translocation of p21 in a dose-dependent matter in myoblasts as compared to myotubes. Apoptosis, as indicated by TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling, was greater in C2C12 myoblasts as compared to myotubes (P<.05) after treatment with H2O2. Caspase-9, -8 and -3 activities were elevated significantly (P<.05) in myoblasts treated with H2O2. Myoblasts were more susceptible to ROS-induced oxidative stress than myotubes. We treated C2C12 myoblasts with 50 μM of resveratrol for periods up to 48 h to determine if myoblasts could be rescued from high-ROS-induced apoptosis by resveratrol. Resveratrol reduced the apoptotic index and significantly reduced the ROS-induced caspase-9, -8 and -3 activity in myoblasts. Furthermore, Bcl-2 and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio were partially rescued in myoblasts by resveratrol treatment. Similarly, muscle stem cells isolated from mouse skeletal muscles showed reduced Sirt1 protein abundance with H2O2 treatment, but this could be reversed by resveratrol. Reduced apoptotic susceptibility in myoblasts as compared to myotubes to ROS is regulated, at least in part, by enhanced p21 promoter activity and nuclear p21 location in myotubes. Resveratrol confers further protection against ROS by improving Sirt1 levels and increasing antioxidant production, which reduces mitochondrial associated apoptotic signaling, and cell death in myoblasts.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Myoblasts; Myogenesis; Myotubes; Oxidative stress; Reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apoptotic signaling induced by H2O2-mediated oxidative stress in differentiated C2C12 myotubes.Life Sci. 2009 Mar 27;84(13-14):468-81. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.01.014. Epub 2009 Feb 3. Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19302811 Free PMC article.
-
Different Antioxidative and Antiapoptotic Effects of Piceatannol and Resveratrol.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021 Mar;376(3):385-396. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.000096. Epub 2020 Dec 17. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021. PMID: 33335015
-
Resveratrol Attenuates Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Injury of Rat Ovarian Granulosa-lutein Cells by Resisting Oxidative Stress via the SIRT1/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(12):947-956. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230403133322. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 37013424
-
Trans-cinnamaldehyde protects C2C12 myoblasts from DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis caused by oxidative stress through inhibiting ROS production.Genes Genomics. 2021 Apr;43(4):303-312. doi: 10.1007/s13258-020-00987-9. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Genes Genomics. 2021. PMID: 32851512
-
Mori Ramulus Suppresses Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Damage in Murine Myoblast C2C12 Cells through Activation of AMPK.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 29;22(21):11729. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111729. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769159 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
C2C12 Mouse Myoblasts Damage Induced by Oxidative Stress Is Alleviated by the Antioxidant Capacity of the Active Substance Phloretin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 11;8:541260. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.541260. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33042989 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Glutathione against Oxidative Stress-induced Cytotoxicity in RAW 264.7 Macrophages through Activating the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor-2/Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Apr 1;8(4):82. doi: 10.3390/antiox8040082. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30939721 Free PMC article.
-
MICU3 regulates mitochondrial Ca2+-dependent antioxidant response in skeletal muscle aging.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Nov 29;12(12):1115. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04400-5. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34845191 Free PMC article.
-
Fucoxanthinol attenuates oxidative stress-induced atrophy and loss in myotubes and reduces the triacylglycerol content in mature adipocytes.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Apr;47(4):2703-2711. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05369-8. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32180086
-
Restoring aged stem cell functionality: Current progress and future directions.Stem Cells. 2020 Sep;38(9):1060-1077. doi: 10.1002/stem.3234. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32473067 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alamdari N, Aversa Z, Castillero E, Gurav A, Petkova V, Tizio S, et al. Resveratrol prevents dexamethasone-induced expression of the muscle atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases atrogin-1 and MuRF1 in cultured myotubes through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;417:528–533. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Allen RG, Tresini M. Oxidative stress and gene regulation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28:463–499. - PubMed
-
- Alway SE, Degens H, Krishnamurthy G, Smith CA. Potential role for Id myogenic repressors in apoptosis and attenuation of hypertrophy in muscles of aged rats. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283:C66–C76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

