SUMOylation of human septins is critical for septin filament bundling and cytokinesis
- PMID: 29051266
- PMCID: PMC5716278
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201703096
SUMOylation of human septins is critical for septin filament bundling and cytokinesis
Abstract
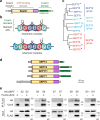
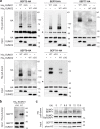
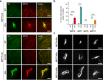
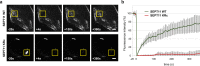
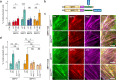
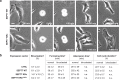
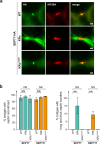
Septins are cytoskeletal proteins that assemble into nonpolar filaments. They are critical in diverse cellular functions, acting as scaffolds for protein recruitment and as diffusion barriers for subcellular compartmentalization. Human septins are encoded by 13 different genes and are classified into four groups based on sequence homology (SEPT2, SEPT3, SEPT6, and SEPT7 groups). In yeast, septins were among the first proteins reported to be modified by SUMOylation, a ubiquitin-like posttranslational modification. However, whether human septins could be modified by small ubiquitin-like modifiers (SUMOs) and what roles this modification may have in septin function remains unknown. In this study, we first show that septins from all four human septin groups can be covalently modified by SUMOs. We show in particular that endogenous SEPT7 is constitutively SUMOylated during the cell cycle. We then map SUMOylation sites to the C-terminal domain of septins belonging to the SEPT6 and SEPT7 groups and to the N-terminal domain of septins from the SEPT3 group. We finally demonstrate that expression of non-SUMOylatable septin variants from the SEPT6 and SEPT7 groups leads to aberrant septin bundle formation and defects in cytokinesis after furrow ingression. Altogether, our results demonstrate a pivotal role for SUMOylation in septin filament bundling and cell division.
© 2017 Ribet et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A draft of the human septin interactome.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 2;5(11):e13799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013799. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21082023 Free PMC article.
-
A revised order of subunits in mammalian septin complexes.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019 Sep;76(9-10):457-466. doi: 10.1002/cm.21569. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 31608568
-
Production and analysis of a mammalian septin hetero-octamer complex.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020 Nov;77(11):485-499. doi: 10.1002/cm.21643. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 33185030 Free PMC article.
-
The Mammalian Septin Interactome.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Feb 7;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2017.00003. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28224124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Actin, microtubule, septin and ESCRT filament remodeling during late steps of cytokinesis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018 Feb;50:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29438904 Review.
Cited by
-
The Structural Biology of Septins and Their Filaments: An Update.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 19;9:765085. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.765085. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34869357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tension-induced cytokinetic abscission in human fibroblasts.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 6;9(10):8999-9009. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24016. eCollection 2018 Feb 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29507669 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling of the oncogenic septin 9 reveals isoform-specific interactions in breast cancer cells.Proteomics. 2021 Oct;21(19):e2100155. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202100155. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34409731 Free PMC article.
-
SUMOylation of periplakin is critical for efficient reorganization of keratin filament network.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Feb 1;30(3):357-369. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-04-0244. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30516430 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin, SUMO, and NEDD8: Key Targets of Bacterial Pathogens.Trends Cell Biol. 2018 Nov;28(11):926-940. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Aug 11. Trends Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30107971 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bertin A., McMurray M.A., Grob P., Park S.S., Garcia G. III, Patanwala I., Ng H.L., Alber T., Thorner J., and Nogales E.. 2008. Saccharomyces cerevisiae septins: supramolecular organization of heterooligomers and the mechanism of filament assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 105:8274–8279. 10.1073/pnas.0803330105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

