Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study
- PMID: 29030361
- PMCID: PMC5867410
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212196
Lack of placental transfer of certolizumab pegol during pregnancy: results from CRIB, a prospective, postmarketing, pharmacokinetic study
Abstract
Objectives: There is a need for effective and safe treatment during pregnancy in women with chronic inflammatory diseases. This study evaluated placental transfer of certolizumab pegol (CZP), an Fc-free anti-tumour necrosis factor drug, from CZP-treated pregnant women to their infants.
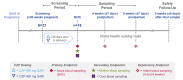
Methods: CRIB was a pharmacokinetic (PK) study of women ≥30 weeks pregnant receiving commercial CZP for a locally approved indication (last dose ≤35 days prior to delivery). Blood samples were collected from mothers, umbilical cords and infants at delivery, and infants again at weeks 4 and 8 post-delivery. CZP plasma concentrations were measured with a highly sensitive and CZP-specific electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (lower limit of quantification 0.032 μg/mL).
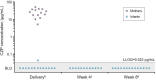
Results: Sixteen women entered and completed the study. Maternal CZP plasma levels at delivery were within the expected therapeutic range (median [range] 24.4 [5.0-49.4] μg/mL). Of the 16 infants, 2 were excluded from the per-protocol set: 1 due to missing data at birth and 1 due to implausible PK data. Of the remaining 14 infants, 13 had no quantifiable CZP levels at birth (<0.032 μg/mL), and 1 had a minimal CZP level of 0.042 μg/mL (infant/mother plasma ratio 0.0009); no infants had quantifiable CZP levels at weeks 4 and 8. Of 16 umbilical cord samples, 1 was excluded due to missing data; 3/15 had quantifiable CZP levels (maximum 0.048 μg/mL).
Conclusions: There was no to minimal placental transfer of CZP from mothers to infants, suggesting lack of in utero foetal exposure during the third trimester. These results support continuation of CZP treatment during pregnancy, when considered necessary.
Trial registration number: NCT02019602; Results.
Keywords: anti-tnf; psoriatic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis; spondyloarthritis; treatment.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2018. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: XM: grant/research support: Biogen, Pfizer, UCB Pharma; consultant for BMS, GSK, LFB, Pfizer, UCB Pharma. FF: grant/research support: UCB Pharma; speaker’s fees: Mepha, Roche, UCB Pharma. BA: grant/research support: Janssen-Cilag, UCB Pharma; speaker’s fees: AbbVie, American Reagent, Janssen-Cilag, UCB Pharma. AF: grant/research support: UCB Pharma. AM: grant/research support: MSD, AbbVie, Pfizer and UCB Pharma; consultant for: MSD, AbbVie, Pfizer, UCB Pharma. R-MF: grant/research support and consultant for: UCB Pharma. AvT: grant/research support: Pfizer, AbbVie, UCB Pharma, Janssen-Cilag, Celgene, Novartis; speaker’s fees: MSD, Janssen-Cilag, Pfizer; consultant for: AbbVie, Novartis, Janssen-Cilag, Pfizer. LS: employee of UCB Pharma. JS: employee of UCB Pharma. MT: employee of UCB Pharma. EH: employee of UCB Pharma. MW: employee of UCB Pharma. EC: grant/research support: UCB Pharma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Minimal to no transfer of certolizumab pegol into breast milk: results from CRADLE, a prospective, postmarketing, multicentre, pharmacokinetic study.Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Nov;76(11):1890-1896. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211384. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017. PMID: 28814432 Free PMC article.
-
Certolizumab treatment during late pregnancy in patients with rheumatic diseases: Low drug levels in cord blood but possible risk for maternal infections. A case series of 13 patients.Joint Bone Spine. 2016 May;83(3):341-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2015.07.004. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Joint Bone Spine. 2016. PMID: 26617214
-
Pregnancy Outcomes After Exposure to Certolizumab Pegol: Updated Results From a Pharmacovigilance Safety Database.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Sep;70(9):1399-1407. doi: 10.1002/art.40508. Epub 2018 Jul 22. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29623679 Free PMC article.
-
New Approaches in Tumor Necrosis Factor Antagonism for the Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis: Certolizumab Pegol.J Rheumatol Suppl. 2015 Nov;93:70-2. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150641. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2015. PMID: 26523062 Review.
-
Certolizumab pegol and secukinumab for treating active psoriatic arthritis following inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2017 Oct;21(56):1-326. doi: 10.3310/hta21560. Health Technol Assess. 2017. PMID: 28976302 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Psoriasis Decision Tree.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021 Apr;14(4):14-22. Epub 2021 Apr 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34055182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapy of PsO in Special Subsets of Patients.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 10;10(11):2879. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112879. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[New antirheumatics : Advances for patients and society].Z Rheumatol. 2018 May;77(4):290-296. doi: 10.1007/s00393-018-0453-2. Z Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29728806 Review. German.
-
A quantitative systems pharmacology model for certolizumab pegol treatment in moderate-to-severe psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 20;14:1212981. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1212981. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37809085 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Efficacy of Biologic Therapies in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Systematic Literature Review and an Enhanced Multinomial Network Meta-Analysis.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021 Dec;11(6):1965-1998. doi: 10.1007/s13555-021-00602-z. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2021. PMID: 34549383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kavanaugh A, Cush JJ, Ahmed MS, et al. . Proceedings from the American College of Rheumatology Reproductive Health Summit: the management of fertility, pregnancy, and lactation in women with autoimmune and systemic inflammatory diseases. Arthritis Care Res 2015;67:313–25. 10.1002/acr.22516 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
