The regulatory effects of fish oil and chitosan on hepatic lipogenic signals in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
- PMID: 28987369
- PMCID: PMC9328862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.11.015
The regulatory effects of fish oil and chitosan on hepatic lipogenic signals in high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Abstract
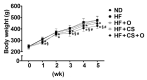
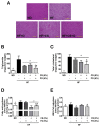
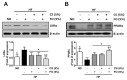
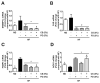
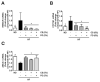
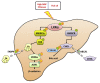
The present study investigated the regulatory effects of fish oil and chitosan on the signals of hepatic lipid metabolism and the postulated mechanism in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. Diet supplementation of chitosan and fish oil efficiently suppressed the increased weights in body and livers of high-fat diet-fed rats. Supplementation of chitosan and fish oil significantly decreased the activities of hepatic lipid biosynthesis-related enzymes and efficiently regulated plasma lipoprotein homeostasis. Both chitosan and fish oil significantly ameliorated the alterations in the protein expressions of hepatic lipogenic transcription factors (LXRα and PPARα), and could also significantly regulate the downstream hepatic lipogenic genes (FAS, HMGCR, CYP7A1, FATP, FABP, AOX, and ABCA) expressions in high-fat diet-fed rats. These results suggest that both fish oil and chitosan exerts downregulative effects on hepatic lipid metabolism in high-fat diet-induced obese rats via the LXRα inhibition and PPARα activation, which further affect the expressions of hepatic lipogenesis-associated genes.
Keywords: chitosan; fish oil; gene expressions; high-fat diet; lipogenesis.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional Comparison of High and Low Molecular Weight Chitosan on Lipid Metabolism and Signals in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jul 29;16(8):251. doi: 10.3390/md16080251. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30060615 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effects and Mechanisms of Chitosan and Its Derivatives on Hypercholesterolemia in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 21;21(1):92. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010092. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31877743 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of chitosan alleviates high-fat diet-enhanced lipogenesis in rats via adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase activation and inhibition of lipogenesis-associated genes.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Mar 25;63(11):2979-88. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00198. Epub 2015 Mar 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25756465
-
Fish Oil Supplementation Alleviates the Altered Lipid Homeostasis in Blood, Liver, and Adipose Tissues in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Apr 25;66(16):4118-4128. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00529. Epub 2018 Apr 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 29627983
-
Effective Food Ingredients for Fatty Liver: Soy Protein β-Conglycinin and Fish Oil.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 18;19(12):4107. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124107. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30567368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Functional Comparison of High and Low Molecular Weight Chitosan on Lipid Metabolism and Signals in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Mar Drugs. 2018 Jul 29;16(8):251. doi: 10.3390/md16080251. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30060615 Free PMC article.
-
Resistant Maltodextrin Ameliorates Altered Hepatic Lipid Homeostasis via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase in a High-Fat Diet-Fed Rat Model.Nutrients. 2019 Jan 29;11(2):291. doi: 10.3390/nu11020291. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30699992 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Comparison for Lipid Metabolism and Intestinal and Fecal Microflora Enzyme Activities between Low Molecular Weight Chitosan and Chitosan Oligosaccharide in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Rats.Mar Drugs. 2017 Jul 24;15(7):234. doi: 10.3390/md15070234. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 28737708 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Marine-Based Nutraceuticals and Their Health Benefits.Mar Drugs. 2020 Dec 9;18(12):627. doi: 10.3390/md18120627. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33317025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Effects and Mechanisms of Chitosan and Its Derivatives on Hypercholesterolemia in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 21;21(1):92. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010092. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31877743 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Obesity and overweight. 2015. [Accessed 4 April 2016]. Available at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
-
- Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, Marks JS. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA. 2003;289(1):76–9. - PubMed
-
- Lewis GF, Uffelman KD, Szeto LW, Steiner G. Effects of acute hyperinsulinemia on VLDL triglyceride and VLDL apoB production in normal weight and obese individuals. Diabetes. 1993;42(6):833–42. - PubMed
-
- Adams LA, Angulo P. Recent concepts in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabet Med. 2005;22(9):1129–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
