Restoration of DAP Kinase Tumor Suppressor Function: A Therapeutic Strategy to Selectively Induce Apoptosis in Cancer Cells Using Immunokinase Fusion Proteins
- PMID: 28976934
- PMCID: PMC5744083
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines5040059
Restoration of DAP Kinase Tumor Suppressor Function: A Therapeutic Strategy to Selectively Induce Apoptosis in Cancer Cells Using Immunokinase Fusion Proteins
Abstract
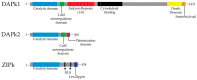
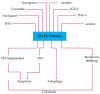
Targeted cancer immunotherapy is designed to selectively eliminate tumor cells without harming the surrounding healthy tissues. The death-associated protein kinases (DAPk) are a family of proapoptotic proteins that play a vital role in the regulation of cellular process and have been identified as positive mediators of apoptosis via extrinsic and intrinsic death-regulating signaling pathways. Tumor suppressor activities have been shown for DAPk1 and DAPk2 and they are downregulated in e.g., Hodgkin's (HL) and B cell lymphoma (CLL), respectively. Here, we review a targeted therapeutic approach which involves reconstitution of DAPks by the generation of immunokinase fusion proteins. These recombinant proteins consist of a disease-specific ligand fused to a modified version of DAPk1 or DAPk2. HL was targeted via CD30 and B-CLL via CD22 cell surface antigens.
Keywords: apoptosis inducers; cancer immunotherapy; death-associated protein kinases (DAPk); humanised cytolytic fusion proteins (hCFPs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mallipeddi R., Wessagowit V., South A.P., Robson A.M., Orchard G.E., Eady R.A., McGrath J.A. Reduced expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in squamous cell carcinoma complicating recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004;122:1302–1309. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.22525.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

