Expression and regulation of the neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 in rat small intestine
- PMID: 28915252
- PMCID: PMC5600382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184845
Expression and regulation of the neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 in rat small intestine
Abstract
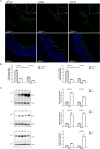
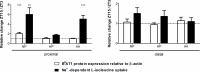
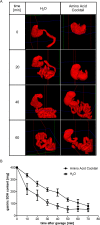
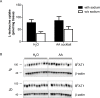
Absorption of neutral amino acids across the luminal membrane of intestinal enterocytes is mediated by the broad neutral amino acid transporter B0AT1 (SLC6A19). Its intestinal expression depends on co-expression of the membrane-anchored peptidase angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and is additionally enhanced by aminopeptidase N (CD13). We investigated in this study the expression of B0AT1 and its auxiliary peptidases as well as its transport function along the rat small intestine. Additionally, we tested its possible short- and long-term regulation by dietary proteins and amino acids. We showed by immunofluorescence that B0AT1, ACE2 and CD13 co-localize on the luminal membrane of small intestinal villi and by Western blotting that their protein expression increases in distal direction. Furthermore, we observed an elevated transport activity of the neutral amino acid L-isoleucine during the nocturnal active phase compared to the inactive one. Gastric emptying was delayed by intragastric application of an amino acid cocktail but we observed no acute dietary regulation of B0AT1 protein expression and L-isoleucine transport. Investigation of the chronic dietary regulation of B0AT1, ACE2 and CD13 by different diets revealed an increased B0AT1 protein expression under amino acid-supplemented diet in the proximal section but not in the distal one and for ACE2 protein expression a reverse localization of the effect. Dietary regulation for CD13 protein expression was not as distinct as for the two other proteins. Ring uptake experiments showed a tendency for increased L-isoleucine uptake under amino acid-supplemented diet and in vivo L-isoleucine absorption was more efficient under high protein and amino acid-supplemented diet. Additionally, plasma levels of branched-chain amino acids were elevated under high protein and amino acid diet. Taken together, our experiments did not reveal an acute amino acid-induced regulation of B0AT1 but revealed a chronic dietary adaptation mainly restricted to the proximal segment of the small intestine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
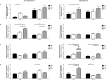
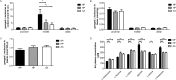
Similar articles
-
ACE2 and gut amino acid transport.Clin Sci (Lond). 2020 Nov 13;134(21):2823-2833. doi: 10.1042/CS20200477. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020. PMID: 33140827 Review.
-
Defective intestinal amino acid absorption in Ace2 null mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Sep 15;303(6):G686-95. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00140.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22790597
-
Human intestine luminal ACE2 and amino acid transporter expression increased by ACE-inhibitors.Amino Acids. 2015 Apr;47(4):693-705. doi: 10.1007/s00726-014-1889-6. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Amino Acids. 2015. PMID: 25534429
-
Expression of apical Na(+)-L-glutamine co-transport activity, B(0)-system neutral amino acid co-transporter (B(0)AT1) and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 along the jejunal crypt-villus axis in young pigs fed a liquid formula.Amino Acids. 2016 Jun;48(6):1491-508. doi: 10.1007/s00726-016-2210-7. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Amino Acids. 2016. PMID: 26984322
-
Collectrin and ACE2 in renal and intestinal amino acid transport.Channels (Austin). 2011 Sep-Oct;5(5):410-23. doi: 10.4161/chan.5.5.16470. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Channels (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21814048 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a Potential Peptide Inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 Targeting its Entry into the Host Cells.Drugs R D. 2020 Sep;20(3):161-169. doi: 10.1007/s40268-020-00312-5. Drugs R D. 2020. PMID: 32592145 Free PMC article.
-
Specific ACE2 expression in small intestinal enterocytes may cause gastrointestinal symptoms and injury after 2019-nCoV infection.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jul;96:19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.027. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32311451 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nanotechnology in current COVID-19 outbreak.Heliyon. 2021 Apr;7(4):e06841. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06841. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33880422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Glycine Supplementation in Drinking Water on the Growth Performance, Intestinal Development, and Genes Expression in the Jejunum of Chicks.Animals (Basel). 2023 Oct 5;13(19):3109. doi: 10.3390/ani13193109. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835714 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and COVID-19 in cardiorenal diseases.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Jan 15;135(1):1-17. doi: 10.1042/CS20200482. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33399851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verrey F, Ristic Z, Romeo E, Ramadan T, Makrides V, Dave MH et al. Novel renal amino acid transporters. Annu Rev Physiol 2005; 67:557–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.67.031103.153949 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hediger MA, Romero MF, Peng J-B, Rolfs A, Takanaga H, Bruford EA. The ABCs of solute carriers: physiological, pathological and therapeutic implications of human membrane transport proteinsIntroduction. Pflugers Arch 2004; 447(5):465–8. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1192-y - DOI - PubMed
-
- Romeo E, Dave MH, Bacic D, Ristic Z, Camargo SMR, Loffing J et al. Luminal kidney and intestine SLC6 amino acid transporters of B0AT-cluster and their tissue distribution in Mus musculus. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2006; 290(2):F376–83. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00286.2005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Broer A, Klingel K, Kowalczuk S, Rasko JEJ, Cavanaugh J, Broer S. Molecular cloning of mouse amino acid transport system B0, a neutral amino acid transporter related to Hartnup disorder. J Biol Chem 2004; 279(23):24467–76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400904200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bohmer C, Broer A, Munzinger M, Kowalczuk S, Rasko JEJ, Lang F et al. Characterization of mouse amino acid transporter B0AT1 (slc6a19). Biochem J 2005; 389(Pt 3):745–51. doi: 10.1042/BJ20050083 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

