Protective efficacy of phosphodiesterase-1 inhibition against alpha-synuclein toxicity revealed by compound screening in LUHMES cells
- PMID: 28904388
- PMCID: PMC5597612
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11664-5
Protective efficacy of phosphodiesterase-1 inhibition against alpha-synuclein toxicity revealed by compound screening in LUHMES cells
Abstract
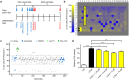
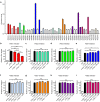
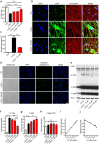
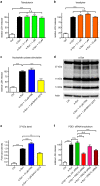
α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity is a core pathogenic event in neurodegenerative synucleinopathies such as Parkinson's disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, or multiple system atrophy. There is currently no disease-modifying therapy available for these diseases. We screened 1,600 FDA-approved drugs for their efficacy to protect LUHMES cells from degeneration induced by wild-type α-synuclein and identified dipyridamole, a non-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitor, as top hit. Systematic analysis of other phosphodiesterase inhibitors identified a specific phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitor as most potent to rescue from α-synuclein toxicity. Protection was mediated by an increase of cGMP and associated with the reduction of a specific α-synuclein oligomeric species. RNA interference experiments confirmed PDE1A and to a smaller extent PDE1C as molecular targets accounting for the protective efficacy. PDE1 inhibition also rescued dopaminergic neurons from wild-type α-synuclein induced degeneration in the substantia nigra of mice. In conclusion, this work identifies inhibition of PDE1A in particular as promising target for neuroprotective treatment of synucleinopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
G.U.H., M.H., and T.W.R. applied for a patent describing PDE1 inhibition as therapeutical approach for synucleinopathies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Small molecule inhibits α-synuclein aggregation, disrupts amyloid fibrils, and prevents degeneration of dopaminergic neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 9;115(41):10481-10486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804198115. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30249646 Free PMC article.
-
Nortriptyline inhibits aggregation and neurotoxicity of alpha-synuclein by enhancing reconfiguration of the monomeric form.Neurobiol Dis. 2017 Oct;106:191-204. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2017.07.007. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2017. PMID: 28711409 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibition Attenuates MPTP-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic System: Involvement of α-Synuclein Aggregation and ER Stress.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Jan;55(1):138-144. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0726-9. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28822080
-
Cellular models of alpha-synuclein toxicity and aggregation.J Neurochem. 2019 Sep;150(5):566-576. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14806. Epub 2019 Jul 30. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31265132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward the discovery and development of effective modulators of α-synuclein amyloid aggregation.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Apr 1;167:10-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.01.045. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30743095 Review.
Cited by
-
A Parkinson's Disease-relevant Mitochondrial and Neuronal Morphology High-throughput Screening Assay in LUHMES Cells.Bio Protoc. 2021 Jan 5;11(1):e3881. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3881. eCollection 2021 Jan 5. Bio Protoc. 2021. PMID: 33732769 Free PMC article.
-
Unbiased Screens for Modifiers of Alpha-Synuclein Toxicity.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019 Feb 9;19(2):8. doi: 10.1007/s11910-019-0925-z. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30739256 Review.
-
Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived 3D-Neurospheres are Suitable for Neurotoxicity Screening.Cells. 2020 May 1;9(5):1122. doi: 10.3390/cells9051122. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32369990 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's Disease: Biomarkers, Treatment, and Risk Factors.Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 30;12:612. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00612. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30214392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease modification in Parkinsonism: obstacles and ways forward.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022 Sep;129(9):1133-1153. doi: 10.1007/s00702-022-02520-6. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2022. PMID: 35695938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fox SH, et al. The Movement Disorder Society Evidence-Based Medicine Review Update: Treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Movement disorders: official journal of the Movement Disorder Society. 2011;26(Suppl 3):41. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, et al. Staging of the intracerebral inclusion body pathology associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (preclinical and clinical stages) Journal of neurology. 2002;249(Suppl 3):3–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

