Concentration dependent chromatin states induced by the bicoid morphogen gradient
- PMID: 28891464
- PMCID: PMC5624782
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.28275
Concentration dependent chromatin states induced by the bicoid morphogen gradient
Abstract
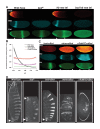
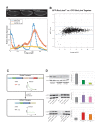
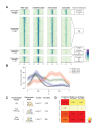
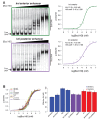
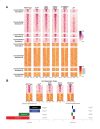
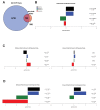
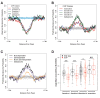
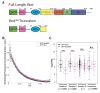
In Drosophila, graded expression of the maternal transcription factor Bicoid (Bcd) provides positional information to activate target genes at different positions along the anterior-posterior axis. We have measured the genome-wide binding profile of Bcd using ChIP-seq in embryos expressing single, uniform levels of Bcd protein, and grouped Bcd-bound targets into four classes based on occupancy at different concentrations. By measuring the biochemical affinity of target enhancers in these classes in vitro and genome-wide chromatin accessibility by ATAC-seq, we found that the occupancy of target sequences by Bcd is not primarily determined by Bcd binding sites, but by chromatin context. Bcd drives an open chromatin state at a subset of its targets. Our data support a model where Bcd influences chromatin structure to gain access to concentration-sensitive targets at high concentrations, while concentration-insensitive targets are found in more accessible chromatin and are bound at low concentrations. This may be a common property of developmental transcription factors that must gain early access to their target enhancers while the chromatin state of the genome is being remodeled during large-scale transitions in the gene regulatory landscape.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; chromatin; chromosomes; developmental biology; genes; morphogen; stem cells; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anterior-posterior positional information in the absence of a strong Bicoid gradient.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Mar 10;106(10):3823-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807878105. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19237583 Free PMC article.
-
Bicoid determines sharp and precise target gene expression in the Drosophila embryo.Curr Biol. 2005 Nov 8;15(21):1888-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.046. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16271865
-
A feed-forward relay integrates the regulatory activities of Bicoid and Orthodenticle via sequential binding to suboptimal sites.Genes Dev. 2018 May 1;32(9-10):723-736. doi: 10.1101/gad.311985.118. Epub 2018 May 15. Genes Dev. 2018. PMID: 29764918 Free PMC article.
-
On the importance of protein diffusion in biological systems: The example of the Bicoid morphogen gradient.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017 Nov;1865(11 Pt B):1676-1686. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2017. PMID: 28919007 Review.
-
Dynamic maternal gradients and morphogenetic networks in Drosophila early embryo.Biosystems. 2018 Nov;173:207-213. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Biosystems. 2018. PMID: 30315821 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Regulation and Cellular Metabolism: An Essential Partnership.Trends Genet. 2021 Apr;37(4):389-400. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2020.09.018. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Trends Genet. 2021. PMID: 33092903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic inheritance and gene expression regulation in early Drosophila embryos.EMBO Rep. 2024 Oct;25(10):4131-4152. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00245-z. Epub 2024 Sep 16. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39285248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal control of gene expression by the pioneer factor Zelda through transient interactions in hubs.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 5;9(1):5194. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07613-z. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30518940 Free PMC article.
-
Trading bits in the readout from a genetic network.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 16;118(46):e2109011118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109011118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34772813 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal Decoding of Cellular Identities in a Genetic Network.Cell. 2019 Feb 7;176(4):844-855.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30712870 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

