Eribulin alone or in combination with the PLK1 inhibitor BI 6727 triggers intrinsic apoptosis in Ewing sarcoma cell lines
- PMID: 28881742
- PMCID: PMC5581041
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17190
Eribulin alone or in combination with the PLK1 inhibitor BI 6727 triggers intrinsic apoptosis in Ewing sarcoma cell lines
Abstract
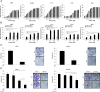
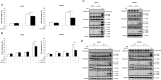
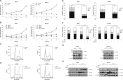
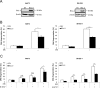
In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms of eribulin-induced cell death and its therapeutic potential in combination with the PLK1 inhibitor BI 6727 in Ewing sarcoma (ES). Here, we show that eribulin triggers cell death in a dose-dependent manner in a panel of ES cell lines. In addition, eribulin at subtoxic, low nanomolar concentrations acts in concert with BI 6727 to induce cell death and to suppress long-term clonogenic survival. Mechanistic studies reveal that eribulin monotherapy at cytotoxic concentrations and co-treatment with eribulin at subtoxic concentrations together with BI 6727 arrest cells in the M phase of the cell cycle prior to the onset of cell death. This mitotic arrest is followed by increased phosphorylation of BCL-2 and BCL-xL as well as downregulation of MCL-1, suggesting inactivation of these antiapoptotic BCL-2 family proteins. Consistently, eribulin monotherapy and eribulin/BI 6727 co-treatment trigger activation of BAX, a key proapoptotic BCL-2 family protein, and increase proteolytic activation of caspase-9 and -3. Importantly, overexpression of BCL-2 or addition of the broad-range caspase inhibitor zVAD.fmk significantly rescue eribulin- as well as eribulin/BI 6727-induced cell death. Together, these findings demonstrate that eribulin induces cell death via the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in ES cells, both alone at cytotoxic concentrations and in combination with BI 6727 at subtoxic concentrations. Thus, our study highlights the therapeutic potential of eribulin for the treatment of ES alone or in rational combination therapies.
Keywords: Ewing sarcoma; PLK1; apoptosis; eribulin.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST None to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic induction of apoptosis by a polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor and microtubule-interfering drugs in Ewing sarcoma cells.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jan 15;138(2):497-506. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29725. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26260582
-
Eribulin synergizes with Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitors to induce apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma.Cancer Lett. 2015 Aug 28;365(1):37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.011. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25917079
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition sensitizes neuroblastoma cells for vinca alkaloid-induced apoptosis.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):8700-11. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3901. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26046302 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of synthetic lethality of PLK1 inhibition and microtubule-destabilizing drugs.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):1946-56. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.59. Epub 2015 May 29. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 26024389 Free PMC article.
-
The Bcl-xL and Bax-alpha control points: modulation of apoptosis induced by cancer chemotherapy and relation to TPCK-sensitive protease and caspase activation.Biochem Cell Biol. 1997;75(4):301-14. Biochem Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9493953 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of PLK1 as a New Therapeutic Target in Mucinous Ovarian Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Mar 13;12(3):672. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030672. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32183025 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin and reactive oxygen species inhibit protein synthesis and regulate the level of the PLK1 protein in Ewing sarcoma cells.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 12;14:1394653. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1394653. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38933441 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging novel agents for patients with advanced Ewing sarcoma: a report from the Children's Oncology Group (COG) New Agents for Ewing Sarcoma Task Force.F1000Res. 2019 Apr 15;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-493. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.18139.1. eCollection 2019. F1000Res. 2019. PMID: 31031965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of Eribulin Plus Gemcitabine Combination in L-Sarcomas.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):680. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010680. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614121 Free PMC article.
-
PLK1 inhibition-based combination therapies for cancer management.Transl Oncol. 2022 Feb;16:101332. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101332. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 34973570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Iwamoto Y. Diagnosis and treatment of Ewing’s sarcoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2007;37:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Esiashvili N, Goodman M, Marcus RB., Jr Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over the past 3 decades: Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results data. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008;30:425–430. - PubMed
-
- Gaspar N, Hawkins DS, Dirksen U, Lewis IJ, Ferrari S, Le Deley MC, Kovar H, Grimer R, Whelan J, Claude L, Delattre O, Paulussen M, Picci P, et al. Ewing Sarcoma: Current Management and Future Approaches Through Collaboration. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:3036–3046. - PubMed
-
- Potratz J, Dirksen U, Jurgens H, Craft A. Ewing sarcoma: clinical state-of-the-art. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2012;29:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

