Targeting Bacterial Cardiolipin Enriched Microdomains: An Antimicrobial Strategy Used by Amphiphilic Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
- PMID: 28878347
- PMCID: PMC5587548
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-10543-3
Targeting Bacterial Cardiolipin Enriched Microdomains: An Antimicrobial Strategy Used by Amphiphilic Aminoglycoside Antibiotics
Abstract
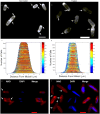
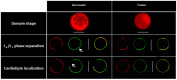
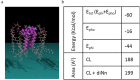
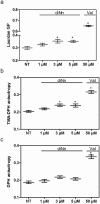
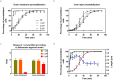
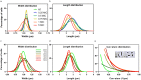
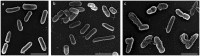
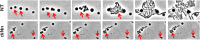
Some bacterial proteins involved in cell division and oxidative phosphorylation are tightly bound to cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is a non-bilayer anionic phospholipid found in bacterial inner membrane. It forms lipid microdomains located at the cell poles and division plane. Mechanisms by which microdomains are affected by membrane-acting antibiotics and the impact of these alterations on membrane properties and protein functions remain unclear. In this study, we demonstrated cardiolipin relocation and clustering as a result of exposure to a cardiolipin-acting amphiphilic aminoglycoside antibiotic, the 3',6-dinonyl neamine. Changes in the biophysical properties of the bacterial membrane of P. aeruginosa, including decreased fluidity and increased permeability, were observed. Cardiolipin-interacting proteins and functions regulated by cardiolipin were impacted by the amphiphilic aminoglycoside as we demonstrated an inhibition of respiratory chain and changes in bacterial shape. The latter effect was characterized by the loss of bacterial rod shape through a decrease in length and increase in curvature. It resulted from the effect on MreB, a cardiolipin dependent cytoskeleton protein as well as a direct effect of 3',6-dinonyl neamine on cardiolipin. These results shed light on how targeting cardiolipin microdomains may be of great interest for developing new antibacterial therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amphiphilic Aminoglycosides as Medicinal Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 8;21(19):7411. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197411. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33049963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of cardiolipin on the antimicrobial activity of a new amphiphilic aminoglycoside derivative on Pseudomonas aeruginosa.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 20;13(8):e0201752. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201752. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30125281 Free PMC article.
-
Negatively Charged Lipids as a Potential Target for New Amphiphilic Aminoglycoside Antibiotics: A BIOPHYSICAL STUDY.J Biol Chem. 2016 Jun 24;291(26):13864-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.665364. Epub 2016 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27189936 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of amphiphilic neamine derivatives: Understanding the mechanism of action on Gram-positive bacteria.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Oct 1;1861(10):182998. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.05.020. Epub 2019 May 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 31153908
-
Molecular mechanisms of membrane targeting antibiotics.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1858(5):980-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Oct 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26514603 Review.
Cited by
-
Fused isoselenazolium salts suppress breast cancer cell growth by dramatic increase in pyruvate-dependent mitochondrial ROS production.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 9;10(1):21595. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78620-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33299068 Free PMC article.
-
Amphiphilic Aminoglycosides as Medicinal Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 8;21(19):7411. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197411. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33049963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of PrsA on membrane lipid composition during daptomycin-resistance-mediated β-lactam sensitization in clinical MRSA strains.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021 Dec 24;77(1):135-147. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkab356. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021. PMID: 34618036 Free PMC article.
-
TTAPE-Me dye is not selective to cardiolipin and binds to common anionic phospholipids nonspecifically.Biophys J. 2021 Sep 7;120(17):3776-3786. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2021.06.039. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 34280369 Free PMC article.
-
Escherichia coli SPFH Membrane Microdomain Proteins HflKC Contribute to Aminoglycoside and Oxidative Stress Tolerance.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0176723. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01767-23. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37347165 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Margalit DN, et al. Targeting cell division: small-molecule inhibitors of FtsZ GTPase perturb cytokinetic ring assembly and induce bacterial lethality. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:11821–11826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404439101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

