The RNA m6A Reader YTHDF2 Is Essential for the Post-transcriptional Regulation of the Maternal Transcriptome and Oocyte Competence
- PMID: 28867294
- PMCID: PMC5613143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.003
The RNA m6A Reader YTHDF2 Is Essential for the Post-transcriptional Regulation of the Maternal Transcriptome and Oocyte Competence
Abstract
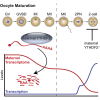
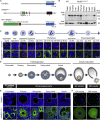
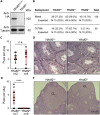
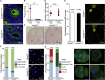
YTHDF2 binds and destabilizes N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-modified mRNA. The extent to which this branch of m6A RNA-regulatory pathway functions in vivo and contributes to mammalian development remains unknown. Here we find that YTHDF2 deficiency is partially permissive in mice and results in female-specific infertility. Using conditional mutagenesis, we demonstrate that YTHDF2 is autonomously required within the germline to produce MII oocytes that are competent to sustain early zygotic development. Oocyte maturation is associated with a wave of maternal RNA degradation, and the resulting relative changes to the MII transcriptome are integral to oocyte quality. The loss of YTHDF2 results in the failure to regulate transcript dosage of a cohort of genes during oocyte maturation, with enrichment observed for the YTHDF2-binding consensus and evidence of m6A in these upregulated genes. In summary, the m6A-reader YTHDF2 is an intrinsic determinant of mammalian oocyte competence and early zygotic development.
Keywords: YTHDF2; m(6)A; m(6)A-reader; maternal transcriptome; oocyte maturation.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differing molecular response of young and advanced maternal age human oocytes to IVM.Hum Reprod. 2017 Nov 1;32(11):2199-2208. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dex284. Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 29025019 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2 is essential for spermatogenesis and fertility by mediating a wave of transcriptional transition in spermatogenic cells.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021 Dec 8;53(12):1702-1712. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmab148. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021. PMID: 34664060
-
Loss of ESRP1 blocks mouse oocyte development and leads to female infertility.Development. 2021 Jan 18;148(2):dev196931. doi: 10.1242/dev.196931. Development. 2021. PMID: 33318146
-
What defines the maternal transcriptome?Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Nov 1;49(5):2051-2062. doi: 10.1042/BST20201125. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34415300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte.Cells. 2020 Mar 9;9(3):662. doi: 10.3390/cells9030662. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32182827 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The regulation and potential roles of m6A modifications in early embryonic development and immune tolerance at the maternal-fetal interface.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 26;13:988130. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.988130. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36225914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physio-pathological effects of m6A modification and its potential contribution to melanoma.Clin Transl Oncol. 2021 Nov;23(11):2269-2279. doi: 10.1007/s12094-021-02644-3. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34105069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mettl3-mediated m6A modification of Fgf16 restricts cardiomyocyte proliferation during heart regeneration.Elife. 2022 Nov 18;11:e77014. doi: 10.7554/eLife.77014. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36399125 Free PMC article.
-
YTHDF2 suppresses the plasmablast genetic program and promotes germinal center formation.Cell Rep. 2022 May 3;39(5):110778. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110778. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35508130 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging function of N6-methyladenosine in cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):5519-5524. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9395. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30344705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bachvarova R., De Leon V., Johnson A., Kaplan G., Paynton B.V. Changes in total RNA, polyadenylated RNA, and actin mRNA during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Dev. Biol. 1985;108:325–331. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

