Mechanisms of Mixed Chimerism-Based Transplant Tolerance
- PMID: 28826941
- PMCID: PMC5669809
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2017.07.008
Mechanisms of Mixed Chimerism-Based Transplant Tolerance
Abstract
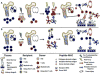
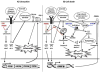
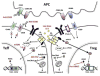
Immune responses to allografts represent a major barrier in organ transplantation. Immune tolerance to avoid chronic immunosuppression is a critical goal in the field, recently achieved in the clinic by combining bone marrow transplantation (BMT) with kidney transplantation following non-myeloablative conditioning. At high levels of chimerism such protocols can permit central deletional tolerance, but with a significant risk of graft-versus-host (GVH) disease (GVHD). By contrast, transient chimerism-based tolerance is devoid of GVHD risk and appears to initially depend on regulatory T cells (Tregs) followed by gradual, presumably peripheral, clonal deletion of donor-reactive T cells. Here we review recent mechanistic insights into tolerance and the development of more robust and safer protocols for tolerance induction that will be guided by innovative immune monitoring tools.
Keywords: clonal deletion; mixed chimerism; regulatory T cells; tolerance.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chimerism-Based Tolerance to Kidney Allografts in Humans: Novel Insights and Future Perspectives.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 5;12:791725. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.791725. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Ex Vivo-Expanded Recipient Regulatory T Cells on Hematopoietic Chimerism and Kidney Allograft Tolerance Across MHC Barriers in Cynomolgus Macaques.Transplantation. 2017 Feb;101(2):274-283. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001559. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 27846155 Free PMC article.
-
[Transplant tolerance through mixed chimerism].Nephrol Ther. 2017 Apr;13 Suppl 1:S127-S130. doi: 10.1016/j.nephro.2017.01.017. Nephrol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28577733 French.
-
T-regulatory cell treatment prevents chronic rejection of heart allografts in a murine mixed chimerism model.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2014 Apr;33(4):429-37. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 28. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2014. PMID: 24468120 Free PMC article.
-
Deletional and regulatory mechanisms coalesce to drive transplantation tolerance through mixed chimerism.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Sep;45(9):2470-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.201545494. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26200095 Review.
Cited by
-
Curative islet and hematopoietic cell transplantation in diabetic mice without toxic bone marrow conditioning.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 8;41(6):111615. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111615. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36351397 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Tolerance Induction by Dendritic Cells In Vivo.Front Immunol. 2018 Feb 26;9:350. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00350. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29535726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Immune Determinants of Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Bidirectional Immune Tolerance in Allogeneic Transplantation.OBM Transplant. 2019;3(1):10.21926/obm.transplant.1901044. doi: 10.21926/obm.transplant.1901044. Epub 2019 Jan 31. OBM Transplant. 2019. PMID: 33511333 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunological Basis of Liver Allograft Rejection.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 2;11:2155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02155. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32983177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Achievement of Tolerance Induction to Prevent Acute Graft-vs.-Host Disease.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 6;10:309. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00309. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30906290 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scandling JD, et al. Tolerance and chimerism after renal and hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(4):362–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

