Interference of Apoptosis by Hepatitis B Virus
- PMID: 28820498
- PMCID: PMC5580487
- DOI: 10.3390/v9080230
Interference of Apoptosis by Hepatitis B Virus
Abstract
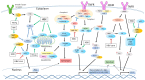
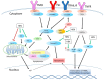
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) causes liver diseases that have been a consistent problem for human health, leading to more than one million deaths every year worldwide. A large proportion of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases across the world are closely associated with chronic HBV infection. Apoptosis is a programmed cell death and is frequently altered in cancer development. HBV infection interferes with the apoptosis signaling to promote HCC progression and viral proliferation. The HBV-mediated alteration of apoptosis is achieved via interference with cellular signaling pathways and regulation of epigenetics. HBV X protein (HBX) plays a major role in the interference of apoptosis. There are conflicting reports on the HBV interference of apoptosis with the majority showing inhibition of and the rest reporting induction of apoptosis. In this review, we described recent studies on the mechanisms of the HBV interference with the apoptosis signaling during the virus infection and provided perspective.
Keywords: X protein; apoptosis; hepatitis B virus (HBV); hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of long non-coding RNAs in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:103-13. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.07.025. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26239319 Review.
-
Linc00152 promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:100-108. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28343069
-
Hepatitis B virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2014 Apr 10;345(2):216-22. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.035. Epub 2013 Aug 25. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 23981576 Review.
-
C-terminal truncated hepatitis B virus X protein promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis through induction of cancer and stem cell-like properties.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 26;7(17):24005-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8209. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27006468 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs associated with HBV infection and HBV-related HCC.Theranostics. 2014 Sep 19;4(12):1176-92. doi: 10.7150/thno.8715. eCollection 2014. Theranostics. 2014. PMID: 25285167 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Crosstalk between Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells and Hepatocytes in Homeostasis and under Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 16;24(20):15212. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015212. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating the Function of Human Jumping Translocation Breakpoint Protein (hJTB) and Its Interacting Partners through In-Solution Proteomics of MCF7 Cells.Molecules. 2022 Nov 28;27(23):8301. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238301. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500393 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Spliced Protein (HBSP) Suppresses Fas-Mediated Hepatocyte Apoptosis via Activation of PI3K/Akt Signaling.J Virol. 2018 Nov 12;92(23):e01273-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01273-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30209179 Free PMC article.
-
HCV- and HBV-mediated liver cancer converge on similar transcriptomic landscapes and immune profiles.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 3:2024.07.01.601493. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.01.601493. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: HGG Adv. 2025 Jan 9;6(1):100373. doi: 10.1016/j.xhgg.2024.100373 PMID: 39005337 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
System Biology Investigation Revealed Lipopolysaccharide and Alcohol-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Resembled Hepatitis B Virus Immunobiology and Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 6;24(13):11146. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311146. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446321 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

