Development of a new analog of SGK1 inhibitor and its evaluation as a therapeutic molecule of colorectal cancer
- PMID: 28819428
- PMCID: PMC5560143
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.19566
Development of a new analog of SGK1 inhibitor and its evaluation as a therapeutic molecule of colorectal cancer
Abstract
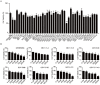
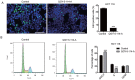
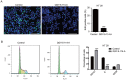
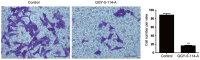
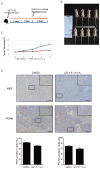
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most leading causes of cancer-related death worldwide. The serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase SGK1 is highly expressed and involved in several tumors. GSK650394, a SGK1 inhibitor, has been proved to be effective in impeding tumor growth in vitro. In this study, we developed a novel analog of GSK650394, and evaluated its effects on CRC cells and tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. HCT116 cells were treated with a concentration gradient of new developed compounds and cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK-8) assay was used to calculate the IC50 value of every analog. Cell proliferation analysis was estimated from EdU staining and flow cytometry in vitro, and immunohistochemistry of Ki67 and PCNA in vivo. Cell migration analysis was examined using the transwell assay. In vivo tumor growth was determined in athymic nude mice by injecting the HCT116 cells in the subcutaneous tissue, followed by the injection of QGY-5-114-A. We found that new developed GSK650394 analog QGY-5-114-A has lower IC50 value, and treatment with QGY-5-114-A significantly inhibited CRC cell proliferation and migration in vitro. Besides that, colonic tumor growth was also dramatically restricted by QGY-5-114-A in vivo. In conclusion, pharmacological treatment with QGY-5-114-A impedes CRC tumor cell proliferation, migration and tumor growth.
Keywords: Cell migration; Cell proliferation; Colonic tumor growth; Colorectal cancer; Inhibitor; Serum and glucocorticoid inducible kinase 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The prospect of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) in cancer therapy: a rising star.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Jul 15;12:1758835920940946. doi: 10.1177/1758835920940946. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32728395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic inhibition of SGK1 suppresses colorectal cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2017 Nov 24;49(11):e399. doi: 10.1038/emm.2017.184. Exp Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 29170478 Free PMC article.
-
An Isoxazole Derivative SHU00238 Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Growth through miRNAs Regulation.Molecules. 2019 Jun 25;24(12):2335. doi: 10.3390/molecules24122335. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31242597 Free PMC article.
-
Esculetin enhances the inhibitory effect of 5-Fluorouracil on the proliferation, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer.Cancer Biomark. 2019;24(2):231-240. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181764. Cancer Biomark. 2019. PMID: 30689555
-
Knockdown of the long non-coding RNA HOTTIP inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation and migration and induces apoptosis by targeting SGK1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Feb;98:286-296. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.064. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29274585
Cited by
-
AGC kinase inhibitors regulate STING signaling through SGK-dependent and SGK-independent mechanisms.Cell Chem Biol. 2023 Dec 21;30(12):1601-1616.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.10.008. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Cell Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37939709 Free PMC article.
-
The prospect of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1) in cancer therapy: a rising star.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020 Jul 15;12:1758835920940946. doi: 10.1177/1758835920940946. eCollection 2020. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32728395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SGK1, autophagy and cancer: an overview.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jan;49(1):675-685. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06836-6. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34669124 Review.
-
Aurora B Inhibitors as Cancer Therapeutics.Molecules. 2023 Apr 11;28(8):3385. doi: 10.3390/molecules28083385. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37110619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and clinicopathological significance of glucocorticoid receptor, SGK1, and NDRG1 in hormone-naïve prostate carcinoma.Med Mol Morphol. 2022 Dec;55(4):283-291. doi: 10.1007/s00795-022-00332-x. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Med Mol Morphol. 2022. PMID: 35861941
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Cappellani A, Zanghi A, Di Vita M, Cavallaro A, Piccolo G, Veroux P. et al. Strong correlation between diet and development of colorectal cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2013;18:190–8. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Remaileh M, Bender S, Raddatz G, Ansari I, Cohen D, Gutekunst J. et al. Chronic inflammation induces a novel epigenetic program that is conserved in intestinal adenomas and in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:2120–30. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

