Capturing the systemic immune signature of a norovirus infection: an n-of-1 case study within a clinical trial
- PMID: 28815218
- PMCID: PMC5531165
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.11300.3
Capturing the systemic immune signature of a norovirus infection: an n-of-1 case study within a clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The infection of a participant with norovirus during the adaptive study of interleukin-2 dose on regulatory T cells in type 1 diabetes (DILT1D) allowed a detailed insight into the cellular and cytokine immune responses to this prevalent gastrointestinal pathogen.
Methods: Serial blood, serum and peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) samples were collected pre-, and post-development of the infection. To differentiate between the immune response to norovirus and to control for the administration of a single dose of aldesleukin (recombinant interleukin-2, rIL-2) alone, samples from five non-infected participants administered similar doses were analysed in parallel.
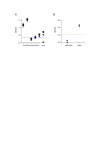
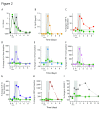
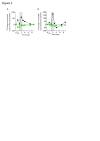
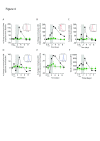
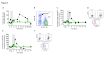
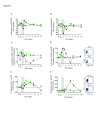
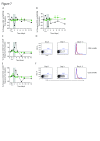
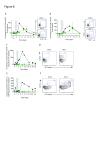
Results: Norovirus infection was self-limited and resolved within 24 hours, with the subsequent development of anti-norovirus antibodies. Serum pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokine levels, including IL-10, peaked during the symptomatic period of infection, coincident with increased frequencies of monocytes and neutrophils. At the same time, the frequency of regulatory CD4 + T cell (Treg), effector T cell (Teff) CD4 + and CD8 + subsets were dynamically reduced, rebounding to baseline levels or above at the next sampling point 24 hours later. NK cells and NKT cells transiently increased CD69 expression and classical monocytes expressed increased levels of CD40, HLA-DR and SIGLEC-1, biomarkers of an interferon response. We also observed activation and mobilisation of Teffs, where increased frequencies of CD69 + and Ki-67 + effector memory Teffs were followed by the emergence of memory CD8 + Teff expressing the mucosal tissue homing markers CD103 and β7 integrin. Treg responses were coincident with the innate cell, Teff and cytokine response. Key Treg molecules FOXP3, CTLA-4, and CD25 were upregulated following infection, alongside an increase in frequency of Tregs with the capacity to home to tissues.
Conclusions: The results illustrate the innate, adaptive and counter-regulatory immune responses to norovirus infection. Low-dose IL-2 administration induces many of the Treg responses observed during infection.
Keywords: Interleukin-2; Proleukin; T regulatory cells; aldesleukin; clinical trial; immune response; norovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: FWL has received fees for consulting and speaking on type 1 diabetes and immunotherapeutics from GlaxoSmithKline, Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epidarex Capital and Hoffmann-La Roche. LSW has received funds to support research from Hoffmann-La Roche and has received consultancy fees from Kymab Access Limited. JAT has received ad hoc consultancy fees from GlaxoSmithKline, AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Janssen and Kymab Limited and is Director of the JDRF/Wellcome Trust Diabetes and Inflammation Laboratory that has received research grant funds from F Hoffmann-La Roche and Eli Lilly.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulatory T Cell Responses in Participants with Type 1 Diabetes after a Single Dose of Interleukin-2: A Non-Randomised, Open Label, Adaptive Dose-Finding Trial.PLoS Med. 2016 Oct 11;13(10):e1002139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002139. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Med. 2016. PMID: 27727279 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
CD4+CD69+ T cells and CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Treg cells imbalance in peripheral blood, spleen and peritoneal lavage from pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) mice.Adv Rheumatol. 2019 Jul 24;59(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s42358-019-0072-x. Adv Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31340848
-
Sex-specific differences in T-cell immune dysregulation and aberrant response to inflammatory stimuli in offspring exposed to maternal chronic inflammation.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2023 Mar;89(3):e13665. doi: 10.1111/aji.13665. Epub 2022 Dec 28. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36504421
-
Thymic commitment of regulatory T cells is a pathway of TCR-dependent selection that isolates repertoires undergoing positive or negative selection.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005;293:43-71. doi: 10.1007/3-540-27702-1_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15981475 Review.
-
Aldesleukin.2018 May 5. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. 2018 May 5. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2012–. PMID: 31643421 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a First Human Norovirus CD8+ T Cell Epitope Restricted to HLA-A*0201 Allele.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 27;9:2782. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02782. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30542352 Free PMC article.
-
The Antigenic Topology of Norovirus as Defined by B and T Cell Epitope Mapping: Implications for Universal Vaccines and Therapeutics.Viruses. 2019 May 10;11(5):432. doi: 10.3390/v11050432. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31083353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Profiling of Immunological Genes during Norovirus Replication in Human Intestinal Enteroids.Viruses. 2021 Jan 21;13(2):155. doi: 10.3390/v13020155. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33494515 Free PMC article.
-
Norovirus encounters in the gut: multifaceted interactions and disease outcomes.Mucosal Immunol. 2019 Nov;12(6):1259-1267. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0199-4. Epub 2019 Sep 9. Mucosal Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31501514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Norovirus in health care and implications for the immunocompromised host.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2019 Aug;32(4):348-355. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000557. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31107251 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

