Bridging the Gap between Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 28796176
- PMCID: PMC5579652
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9080859
Bridging the Gap between Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
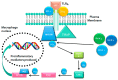
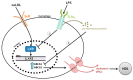
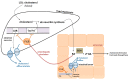
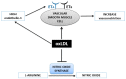
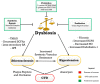
The human gut is heavily colonized by a community of microbiota, primarily bacteria, that exists in a symbiotic relationship with the host and plays a critical role in maintaining host homeostasis. The consumption of a high-fat (HF) diet has been shown to induce gut dysbiosis and reduce intestinal integrity. Recent studies have revealed that dysbiosis contributes to the progression of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) by promoting two major CVD risk factors-atherosclerosis and hypertension. Imbalances in host-microbial interaction impair homeostatic mechanisms that regulate health and can activate multiple pathways leading to CVD risk factor progression. Dysbiosis has been implicated in the development of atherosclerosis through metabolism-independent and metabolite-dependent pathways. This review will illustrate how these pathways contribute to the various stages of atherosclerotic plaque progression. In addition, dysbiosis can promote hypertension through vascular fibrosis and an alteration of vascular tone. As CVD is the number one cause of death globally, investigating the gut microbiota as a locus of intervention presents a novel and clinically relevant avenue for future research, with vast therapeutic potential.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; dysbiosis; gut microbiota; prebiotics; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular diseases.World J Cardiol. 2020 Apr 26;12(4):110-122. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v12.i4.110. World J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32431782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota and Heart, Vascular Injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1238:107-141. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-2385-4_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32323183 Review.
-
The gut microbiota as a novel regulator of cardiovascular function and disease.J Nutr Biochem. 2018 Jun;56:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.12.010. Epub 2017 Dec 27. J Nutr Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29427903 Review.
-
Role of the intestinal microbiome and its therapeutic intervention in cardiovascular disorder.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 26;15:1321395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1321395. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38343539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The gut microbiota and its interactions with cardiovascular disease.Microb Biotechnol. 2020 May;13(3):637-656. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13524. Epub 2020 Jan 26. Microb Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31984651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pathophysiology and genetics of salt-sensitive hypertension.Front Physiol. 2022 Sep 13;13:1001434. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1001434. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36176775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of probiotic supplementation along with calorie restriction on metabolic endotoxemia, and inflammation markers in coronary artery disease patients: a double blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial.Nutr J. 2021 Jun 1;20(1):47. doi: 10.1186/s12937-021-00703-7. Nutr J. 2021. PMID: 34074289 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Early Disruption of the Microbiome Leading to Decreased Antioxidant Capacity and Epigenetic Changes: Implications for the Rise in Autism.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Aug 15;12:256. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00256. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30158857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Probiotics and Prebiotics in the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 15;11(3):635. doi: 10.3390/nu11030635. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30875987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of Spaceflight Induced Changes to Astronaut Microbiomes.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 2;12:659179. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.659179. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34149649 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

