3.3 Å structure of Niemann-Pick C1 protein reveals insights into the function of the C-terminal luminal domain in cholesterol transport
- PMID: 28784760
- PMCID: PMC5576846
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1711716114
3.3 Å structure of Niemann-Pick C1 protein reveals insights into the function of the C-terminal luminal domain in cholesterol transport
Abstract
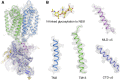
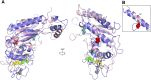
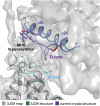
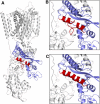
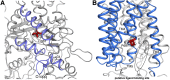
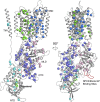
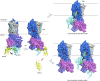
Niemann-Pick C1 (NPC1) and NPC2 proteins are indispensable for the export of LDL-derived cholesterol from late endosomes. Mutations in these proteins result in Niemann-Pick type C disease, a lysosomal storage disease. Despite recent reports of the NPC1 structure depicting its overall architecture, the function of its C-terminal luminal domain (CTD) remains poorly understood even though 45% of NPC disease-causing mutations are in this domain. Here, we report a crystal structure at 3.3 Å resolution of NPC1* (residues 314-1,278), which-in contrast to previous lower resolution structures-features the entire CTD well resolved. Notably, all eight cysteines of the CTD form four disulfide bonds, one of which (C909-C914) enforces a specific loop that in turn mediates an interaction with a loop of the N-terminal domain (NTD). Importantly, this loop and its interaction with the NTD were not observed in any previous structures due to the lower resolution. Our mutagenesis experiments highlight the physiological relevance of the CTD-NTD interaction, which might function to keep the NTD in the proper orientation for receiving cholesterol from NPC2. Additionally, this structure allows us to more precisely map all of the disease-causing mutations, allowing future molecular insights into the pathogenesis of NPC disease.
Keywords: Niemann–Pick type C disease; cholesterol transport; crystal structure; cysteine-rich domain; sterol-sensing domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

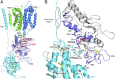
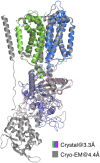
Similar articles
-
Comparative study of the effect of disease causing and benign mutations in position Q92 on cholesterol binding by the NPC1 n-terminal domain.Proteins. 2018 Nov;86(11):1165-1175. doi: 10.1002/prot.25597. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Proteins. 2018. PMID: 30183109 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease: a QM/MM study of conformational changes in cholesterol in the NPC1(NTD) and NPC2 binding pockets.Biochemistry. 2014 Oct 21;53(41):6603-14. doi: 10.1021/bi500548f. Epub 2014 Oct 10. Biochemistry. 2014. PMID: 25251378
-
Molecular dynamics study with mutation shows that N-terminal domain structural re-orientation in Niemann-Pick type C1 is required for proper alignment of cholesterol transport.J Neurochem. 2021 Mar;156(6):967-978. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15150. Epub 2020 Sep 16. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 32880929 Free PMC article.
-
NPC1, intracellular cholesterol trafficking and atherosclerosis.Clin Chim Acta. 2014 Feb 15;429:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.026. Epub 2013 Dec 1. Clin Chim Acta. 2014. PMID: 24296264 Review.
-
Niemann-Pick type C mutations cause lipid traffic jam.Traffic. 2000 Mar;1(3):218-25. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010304.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208105 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Synthesis of Tetrazole- and Pyridine-Containing Itraconazole Analogs as Potent Angiogenesis Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020 Apr 8;11(6):1111-1117. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00438. eCollection 2020 Jun 11. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32550989 Free PMC article.
-
Simulations of NPC1(NTD):NPC2 Protein Complex Reveal Cholesterol Transfer Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Sep 4;19(9):2623. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092623. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30181526 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosomal cholesterol export reconstituted from fragments of Niemann-Pick C1.Elife. 2018 Jul 26;7:e38564. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38564. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30047864 Free PMC article.
-
NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 (NPC1)-mediated cholesterol export from lysosomes.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 1;294(5):1706-1709. doi: 10.1074/jbc.TM118.004165. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30710017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of Tom20 and Tom22 cytosolic domains as the human TOM complex receptors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 28;119(26):e2200158119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2200158119. Epub 2022 Jun 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35733257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown MS, Goldstein JL. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Dana SE, Faust JR, Beaudet AL, Brown MS. Role of lysosomal acid lipase in the metabolism of plasma low density lipoprotein. Observations in cultured fibroblasts from a patient with cholesteryl ester storage disease. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:8487–8495. - PubMed
-
- Naureckiene S, et al. Identification of HE1 as the second gene of Niemann-Pick C disease. Science. 2000;290:2298–2301. - PubMed
-
- Carstea ED, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: Homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Neiss WF. A coat of glycoconjugates on the inner surface of the lysosomal membrane in the rat kidney. Histochemistry. 1984;80:603–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

