Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome
- PMID: 28777303
- PMCID: PMC5578092
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18081702
Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome
Abstract
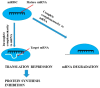
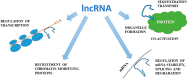
In its early stages, symptoms of chronic kidney disease (CKD) are usually not apparent. Significant reduction of the kidney function is the first obvious sign of disease. If diagnosed early (stages 1 to 3), the progression of CKD can be altered and complications reduced. In stages 4 and 5 extensive kidney damage is observed, which usually results in end-stage renal failure. Currently, the diagnosis of CKD is made usually on the levels of blood urea and serum creatinine (sCr), however, sCr has been shown to be lacking high predictive value. Due to the development of genomics, epigenetics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, the introduction of novel techniques will allow for the identification of novel biomarkers in renal diseases. This review presents some new possible biomarkers in the diagnosis of CKD and in the prediction of outcome, including asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), uromodulin, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), miRNA, ncRNA, and lincRNA biomarkers and proteomic and metabolomic biomarkers. Complicated pathomechanisms of CKD development and progression require not a single marker but their combination in order to mirror all types of alterations occurring in the course of this disease. It seems that in the not so distant future, conventional markers may be exchanged for new ones, however, confirmation of their efficacy, sensitivity and specificity as well as the reduction of analysis costs are required.
Keywords: ADMA; KIM-1; NGAL; SDMA; biomarkers; chronic kidney disease; lincRNA and proteomic and metabolomic biomarkers; miRNA; ncRNA; uromodulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cystatin C and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as Early Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease in Dogs.Top Companion Anim Med. 2021 Nov;45:100580. doi: 10.1016/j.tcam.2021.100580. Epub 2021 Aug 21. Top Companion Anim Med. 2021. PMID: 34428574
-
Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) outperforms asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and other methylarginines as predictor of renal and cardiovascular outcome in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease.Clin Res Cardiol. 2018 Mar;107(3):201-213. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1172-4. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Clin Res Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29101459
-
Biomarkers of renal function, which and when?Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Jan 1;438:350-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.08.039. Epub 2014 Sep 3. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25195004 Review.
-
The Associations of Blood Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin with Progression from CKD to ESRD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Dec 7;11(12):2141-2149. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02670316. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27852662 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with High Salt Intake.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Sep 30;18(10):2080. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102080. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28973979 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Is Accompanied by Local and Systemic Changes in L-arginine/NO Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 30;21(17):6282. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176282. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32872669 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer effect of Cenchrus ciliaris L.Saudi Pharm J. 2018 Nov;26(7):952-955. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2018.05.003. Epub 2018 May 12. Saudi Pharm J. 2018. PMID: 30416351 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide N-Methyl Transferase as a Predictive Marker of Tubular Fibrosis in CKD.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Aug 7;16:3331-3344. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S420706. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37576910 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the relationship between xanthine oxidoreductase activity and chronic kidney disease.iScience. 2023 Jul 10;26(11):107332. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107332. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37927553 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between urinary cysteine-rich protein 61 excretion and kidney function decline in outpatients with chronic kidney disease: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan.BMJ Open. 2021 Oct 6;11(10):e051165. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051165. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34615677 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

