Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: an overview of mechanisms of action and clinical implications
- PMID: 28770011
- PMCID: PMC5527439
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-017-0254-9
Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: an overview of mechanisms of action and clinical implications
Abstract
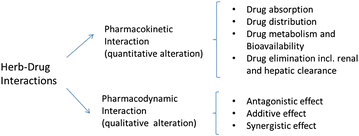
Diabetes is a complex condition with a variety of causes and pathophysiologies. The current single target approach has not provided ideal clinical outcomes for the treatment of the disease and its complications. Herbal medicine has been used for the management of various diseases such as diabetes over centuries. Many diabetic patients are known to use herbal medicines with antidiabetic properties in addition to their mainstream treatments, which may present both a benefit as well as potential risk to effective management of their disease. In this review we evaluate the clinical and experimental literature on herb-drug interactions in the treatment of diabetes. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions between drugs and herbs are discussed, and some commonly used herbs which can interact with antidiabetic drugs summarised. Herb-drug interactions can be a double-edged sword presenting both risks (adverse drug events) and benefits (through enhancement). There is a general lack of data on herb-drug interactions. As such, more rigorous scientific research is urgently needed to guide clinical practice as well as to safeguard the wellbeing of diabetes patients.
Keywords: Antidiabetic drugs; Antidiabetic herbs; Herb–drug interactions; Pharmacodynamics interaction; Pharmacokinetic interaction; Synergism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antidiabetics Interactions with Herbs: A Compressive Review.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2022;18(1):e011221190237. doi: 10.2174/1573399817999210112191718. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2022. PMID: 33438541 Review.
-
Drug-herb interactions: eliminating toxicity with hard drug design.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(35):4649-64. doi: 10.2174/138161206779010440. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 17168768 Review.
-
Herb-Drug Interactions of Commonly Used Chinese Medicinal Herbs.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017;135:197-232. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2017.02.010. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28807159 Review.
-
[Herb-drug enzyme-mediated interactions and the associated experimental methods: a review].J Tradit Chin Med. 2016 Jun;36(3):392-408. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(16)30054-1. J Tradit Chin Med. 2016. PMID: 27468556 Review. Chinese.
-
Could the gut microbiota reconcile the oral bioavailability conundrum of traditional herbs?J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Feb 17;179:253-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.031. Epub 2015 Dec 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26723469 Review.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Medicinal Plants for Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes: An Overview of Meta-Analyses of Clinical Trials.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:777561. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.777561. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of Plu kaow (Houttuynia cordata Thunb.) Ethanolic Extract on Diabetes and Dyslipidemia in STZ Induced Diabetic Rats: Phytochemical Profiling, Cheminformatics Analyses, and Molecular Docking Studies.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;13(9):1064. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091064. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334723 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Approaches to Retinal Health Focusing on Diabetic Retinopathy.Cells. 2023 Nov 24;12(23):2699. doi: 10.3390/cells12232699. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Astragali radix extract on pharmacokinetic behavior of dapagliflozin in healthy and type 2 diabetic rats.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 10;14:1214658. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1214658. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37881186 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS-QTOF Screening and Identification of Phenolic Compounds from Australian Grown Herbs and Their Antioxidant Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 5;10(11):1770. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111770. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahelic D. 7th edition of Idf diabetes Atlas-call for immediate action. Lijec Vjesn. 2016;138(1–2):57–58. - PubMed
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare . Cardiovascular disease, diabetes and chronic kidney disease-Australian facts: mortality. Cardiovascular, diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Canberra: AIHW; 2014.
-
- Haynes RB, Taylor DW, Sackett DL. Compliance in health care. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press; 1979.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials