Cross-talk of Brassinosteroid signaling in controlling growth and stress responses
- PMID: 28751549
- PMCID: PMC6296487
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20160633
Cross-talk of Brassinosteroid signaling in controlling growth and stress responses
Abstract
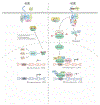
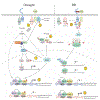
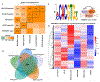
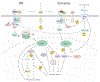
Plants are faced with a barrage of stresses in their environment and must constantly balance their growth and survival. As such, plants have evolved complex control systems that perceive and respond to external and internal stimuli in order to optimize these responses, many of which are mediated by signaling molecules such as phytohormones. One such class of molecules called Brassinosteroids (BRs) are an important group of plant steroid hormones involved in numerous aspects of plant life including growth, development and response to various stresses. The molecular determinants of the BR signaling pathway have been extensively defined, starting with the membrane-localized receptor BRI1 and co-receptor BAK1 and ultimately culminating in the activation of BES1/BZR1 family transcription factors, which direct a transcriptional network controlling the expression of thousands of genes enabling BRs to influence growth and stress programs. Here, we highlight recent progress in understanding the relationship between the BR pathway and plant stress responses and provide an integrated view of the mechanisms mediating cross-talk between BR and stress signaling.
Keywords: Brassinosteroid; cross-talk; drought; innate immunity; plant hormones; plant signal transduction.
© 2017 The Author(s); published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The Authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in the regulation of brassinosteroid signaling and biosynthesis pathways.J Integr Plant Biol. 2011 Jun;53(6):455-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01046.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21554539 Review.
-
WRKY transcription factors are involved in brassinosteroid signaling and mediate the crosstalk between plant growth and drought tolerance.Plant Signal Behav. 2017 Nov 2;12(11):e1365212. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2017.1365212. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Plant Signal Behav. 2017. PMID: 29027842 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Brassinosteroid-Mediated Responses to Changing Environments in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 15;21(8):2737. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082737. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326491 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and networks for brassinosteroid regulated gene expression.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013 Oct;16(5):545-53. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2013.08.002. Epub 2013 Aug 27. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23993372 Review.
-
Linking Brassinosteroid and ABA Signaling in the Context of Stress Acclimation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 20;21(14):5108. doi: 10.3390/ijms21145108. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32698312 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RMD and Its Suppressor MAPK6 Control Root Circumnutation and Obstacle Avoidance via BR Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 30;25(19):10543. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910543. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408870 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Hormonal control of plant stress responses: Brassinosteroids and gibberellin.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jan 18;14:1131398. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1131398. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36743497 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Signaling by the EPFL-ERECTA family coordinates female germline specification through the BZR1 family in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2023 Apr 20;35(5):1455-1473. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad032. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36748257 Free PMC article.
-
BES1 is activated by EMS1-TPD1-SERK1/2-mediated signaling to control tapetum development in Arabidopsis thaliana.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 13;10(1):4164. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12118-4. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31519953 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced genes expression pattern greatly contributes to divergence in Verticillium wilt resistance between Gossypium barbadense and Gossupium hirsutum.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 1;13:979585. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.979585. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35979082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Nagpal P, Vitart V, McMorris TC and Chory J (1996) A role for brassinosteroids in light-dependent development of Arabidopsis. Science 272, 398–401 doi:10.1126/science.272.5260.398 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Szekeres M, Németh K, Koncz-Kálmán Z, Mathur J, Kauschmann A, Altmann T et al. (1996) Brassinosteroids rescue the deficiency of CYP90, a cytochrome P450, controlling cell elongation and de-etiolation in Arabidopsis. Cell 85, 171–182 doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81094-6 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noguchi T, Fujioka S, Takatsuto S, Sakurai A, Yoshida S, Li JM et al. (1999) Arabidopsis det2 is defective in the conversion of (24R)-24-methylcholest-4-En-3-One to (24R)-24-methyl-5α-cholestan-3-one in brassinosteroid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 120, 833–839 doi:10.1104/pp.120.3.833 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clouse SD, Langford M and McMorris TC (1996) A brassinosteroid-insensitive mutant in Arabidopsis thaliana exhibits multiple defects in growth and development. Plant Physiol. 111, 671–678 doi:10.1104/pp.111.3.671 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belkhadir Y and Jaillais Y (2015) The molecular circuitry of brassinosteroid signaling. New Phytol. 206, 522–540 doi:10.1111/nph.13269 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

