Enhanced immunization via dissolving microneedle array-based delivery system incorporating subunit vaccine and saponin adjuvant
- PMID: 28740383
- PMCID: PMC5503490
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S132456
Enhanced immunization via dissolving microneedle array-based delivery system incorporating subunit vaccine and saponin adjuvant
Abstract
Purpose: To enhance the immunogenicity of the model subunit vaccine, ovalbumin (OVA) was combined with platycodin (PD), a saponin adjuvant. To reduce the toxicity of PD, OVA, and adjuvant were loaded together into liposomes before being incorporated into a dissolving microneedle array.
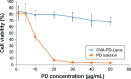
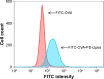
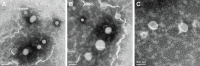
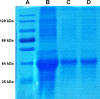
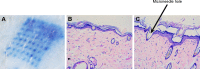
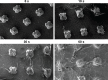
Methods: OVA- and PD-loaded liposomes (OVA-PD-Lipos) were prepared using the film dispersion method. Their uptake behavior, toxicity to mouse bone marrow dendritic cells (BMDCs), and hemolytic activity to rabbit red blood cells (RBCs) were evaluated. The OVA-PD-Lipos were incorporated into a dissolving microneedle array. The chemical stability of OVA and the physical stability of OVA-PD-Lipos in microneedle arrays were investigated. The immune response of Institute of Cancer Research mice and potential skin irritation reaction of rabbits to OVA-PD-Lipos-MNs were evaluated.
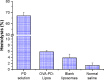
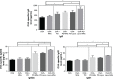
Results: The uptake of OVA by mouse BMDCs was greatly enhanced when OVA was prepared as OVA-PD-Lipos, and in this form, the toxicity of PD was dramatically reduced. OVA was chemically stable as OVA-PD-Lipos, when OVA-PD-Lipos was incorporated into a dissolving microneedle array. Institute of Cancer Research mice treated with OVA-PD-Lipos-MNs showed a significantly enhanced immune response. PD combined with OVA elicited a balanced Th1 and Th2 humoral immune response in mice, with minimal irritation in rabbit skin.
Conclusion: The dissolving microneedle array-based system is a promising delivery vehicle for subunit vaccine and its adjuvant.
Keywords: dissolving microneedle array; intradermal vaccination; liposomes; saponin adjuvant; subunit vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhanced transcutaneous immunization via dissolving microneedle array loaded with liposome encapsulated antigen and adjuvant.Int J Pharm. 2013 Apr 15;447(1-2):22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.02.006. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Int J Pharm. 2013. PMID: 23410987
-
DNA-based vaccination against hepatitis B virus using dissolving microneedle arrays adjuvanted by cationic liposomes and CpG ODN.Drug Deliv. 2016 Sep;23(7):2391-2398. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.992497. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 25625495
-
A fast-dissolving microneedle array loaded with chitosan nanoparticles to evoke systemic immune responses in mice.J Mater Chem B. 2020 Jan 14;8(2):216-225. doi: 10.1039/c9tb02061f. Epub 2019 Dec 5. J Mater Chem B. 2020. PMID: 31803892
-
Dissolving Microneedle Patches for Dermal Vaccination.Pharm Res. 2017 Nov;34(11):2223-2240. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2223-2. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28718050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional particle-constituted microneedle arrays as cutaneous or mucosal vaccine adjuvant-delivery systems.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Aug 2;12(8):2075-2089. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1158368. Epub 2016 May 9. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 27159879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle cancer vaccines: Design considerations and recent advances.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020 Sep;15(5):576-590. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 33193861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress in the development of natural-product-based mucosal vaccine adjuvants.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 5;14:1152855. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1152855. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37090704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microneedle Arrays Combined with Nanomedicine Approaches for Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics.J Clin Med. 2021 Jan 6;10(2):181. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020181. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33419118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging skin-targeted drug delivery strategies to engineer immunity: A focus on infectious diseases.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021 Feb;18(2):151-167. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2021.1823964. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 32924651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Individually coated microneedles for co-delivery of multiple compounds with different properties.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018 Oct;8(5):1043-1052. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0549-x. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29948917 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Drane D, Gittleson C, Boyle J, Maraskovsky E. ISCOMATRIX adjuvant for prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2007;6(5):761–772. - PubMed
-
- Song X, Hu S. Adjuvant activities of saponins from traditional Chinese medicinal herbs. Vaccine. 2009;27(36):4883–4890. - PubMed
-
- Xie Y, Sun HX, Li D. Platycodin D is a potent adjuvant of specific cellular and humoral immune responses against recombinant hepatitis B antigen. Vaccine. 2009;27(5):757–764. - PubMed
-
- Silva JM, Zupancic E, Vandermeulen G, et al. In vivo delivery of peptides and Toll-like receptor ligands by mannose-functionalized polymeric nanoparticles induces prophylactic and therapeutic anti-tumor immune responses in a melanoma model. J Control Release. 2015;198:91–103. - PubMed
-
- Kastenmüller W, Kastenmüller K, Kurts C, et al. Dendritic cell-targeted vaccines – hope or hype? Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(10):705–711. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

