FGF21 Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Cognitive Impairment via Metabolic Regulation and Anti-inflammation of Obese Mice
- PMID: 28712011
- PMCID: PMC5971086
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-017-0663-7
FGF21 Attenuates High-Fat Diet-Induced Cognitive Impairment via Metabolic Regulation and Anti-inflammation of Obese Mice
Abstract
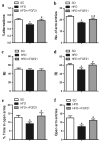
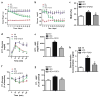
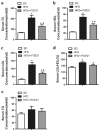
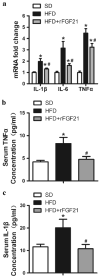
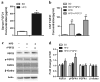
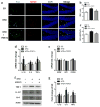
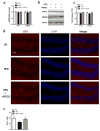
Accumulating studies suggest that overnutrition-associated obesity may lead to development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndromes (MetS). MetS and its components are important risk factors of mild cognitive impairment, age-related cognitive decline, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer's disease. It has been recently proposed that development of a disease-course modification strategy toward early and effective risk factor management would be clinically significant in reducing the risk of metabolic disorder-initiated cognitive decline. In the present study, we propose that fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a novel candidate for the disease-course modification approach. Using a high-fat diet (HFD) consumption-induced obese mouse model, we tested our hypothesis that recombinant human FGF21 (rFGF21) administration is effective for improving obesity-induced cognitive dysfunction and anxiety-like behavior, by its multiple metabolic modulation and anti-pro-inflammation actions. Our experimental findings support our hypothesis that rFGF21 is protective to HFD-induced cognitive impairment, at least in part by metabolic regulation in glucose tolerance impairment, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia; potent systemic pro-inflammation inhibition; and improvement of hippocampal dysfunction, particularly by inhibiting pro-neuroinflammation and neurogenesis deficit. This study suggests that FGF21 might be a novel molecular target of the disease-course-modifying strategy for early intervention of MstS-associated cognitive decline.
Keywords: Cognitive impairment; Fibroblast growth factor 21; High-fat diet; Inflammation; Metabolic disorders; Obese mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
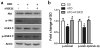
Similar articles
-
FGF21 and DPP-4 inhibitor equally prevents cognitive decline in obese rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jan;97:1663-1672. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.021. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793329
-
Metabolic Stress Alters Antioxidant Systems, Suppresses the Adiponectin Receptor 1 and Induces Alzheimer's Like Pathology in Mice Brain.Cells. 2020 Jan 19;9(1):249. doi: 10.3390/cells9010249. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31963819 Free PMC article.
-
Probucol prevents blood-brain barrier dysfunction and cognitive decline in mice maintained on pro-diabetic diet.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019 Jan;16(1):87-97. doi: 10.1177/1479164118795274. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2019. PMID: 30156119
-
Inflammation and gut-brain axis link obesity to cognitive dysfunction: plausible pharmacological interventions.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017 Dec;37:87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Nov 5. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29107872 Review.
-
Biological role, clinical significance, and therapeutic possibilities of the recently discovered metabolic hormone fibroblastic growth factor 21.Eur J Endocrinol. 2012 Sep;167(3):301-9. doi: 10.1530/EJE-12-0357. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Eur J Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22740503 Review.
Cited by
-
Physical Exercise-Induced Myokines in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5795. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115795. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of myokines in exercise-induced improvement of neuropsychiatric function.Pflugers Arch. 2019 Mar;471(3):491-505. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02253-8. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Pflugers Arch. 2019. PMID: 30627775 Review.
-
Links Between Obesity-Induced Brain Insulin Resistance, Brain Mitochondrial Dysfunction, and Dementia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Aug 31;9:496. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00496. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 30233495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 on Lactate Uptake and Usage in Mice with Diabetes-Associated Cognitive Decline.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Sep;59(9):5656-5672. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02926-z. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35761156
-
FGF21 Depletion Attenuates Colitis through Intestinal Epithelial IL-22-STAT3 Activation in Mice.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 26;15(9):2086. doi: 10.3390/nu15092086. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432218 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

