Inhibition of IKKɛ and TBK1 Improves Glucose Control in a Subset of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 28683283
- PMCID: PMC5663294
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.06.006
Inhibition of IKKɛ and TBK1 Improves Glucose Control in a Subset of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
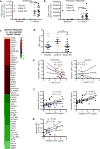
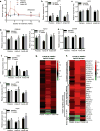
Numerous studies indicate an inflammatory link between obesity and type 2 diabetes. The inflammatory kinases IKKɛ and TBK1 are elevated in obesity; their inhibition in obese mice reduces weight, insulin resistance, fatty liver and inflammation. Here we studied amlexanox, an inhibitor of IKKɛ and TBK1, in a proof-of-concept randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 42 obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Treatment of patients with amlexanox produced a statistically significant reduction in Hemoglobin A1c and fructosamine. Interestingly, a subset of drug responders also exhibited improvements in insulin sensitivity and hepatic steatosis. This subgroup was characterized by a distinct inflammatory gene expression signature from biopsied subcutaneous fat at baseline. They also exhibited a unique pattern of gene expression changes in response to amlexanox, consistent with increased energy expenditure. Together, these data suggest that dual-specificity inhibitors of IKKɛ and TBK1 may be effective therapies for metabolic disease in an identifiable subset of patients.
Keywords: amlexanox; clinical trial; energy expenditure; fatty liver; gene expression; inflammation; obesity; protein kinase.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Amlexanox reversed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through IKKε inhibition of hepatic stellate cell.Life Sci. 2019 Dec 15;239:117010. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117010. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31672578
-
An inhibitor of the protein kinases TBK1 and IKK-ɛ improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunctions in mice.Nat Med. 2013 Mar;19(3):313-21. doi: 10.1038/nm.3082. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23396211 Free PMC article.
-
Dual TBK1/IKKɛ inhibitor amlexanox attenuates the severity of hepatotoxin-induced liver fibrosis and biliary fibrosis in mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jan;24(2):1383-1398. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14817. Epub 2019 Dec 10. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31821710 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of IκB kinases and TANK-binding kinase 1 in hepatic lipid metabolism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Nov;53(11):1697-1705. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00712-w. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34848839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amlexanox: A Novel Therapeutic for Atopic, Metabolic, and Inflammatory Disease.Yale J Biol Med. 2020 Dec 29;93(5):759-763. eCollection 2020 Dec. Yale J Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 33380937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) in cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020 Nov;24(11):1065-1078. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2020.1826929. Epub 2020 Oct 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2020. PMID: 32962465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Kinases in Obesity, and the Kinase-Targeted Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:199-229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287853 Review.
-
Essential Roles for the Non-Canonical IκB Kinases in Linking Inflammation to Cancer, Obesity, and Diabetes.Cells. 2019 Feb 19;8(2):178. doi: 10.3390/cells8020178. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30791439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon signaling, regulation and gene stimulation in chronic virus infection.Semin Immunol. 2019 Jun;43:101277. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2019.05.001. Epub 2019 May 30. Semin Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31155227 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Integrated View of Immunometabolism.Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):22-40. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.025. Cell. 2018. PMID: 29328913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Diabetes, A. Bantle JP, Wylie-Rosett J, Albright AL, Apovian CM, Clark NG, Franz MJ, Hoogwerf BJ, Lichtenstein AH, Mayer-Davis E, et al. Nutrition recommendations and interventions for diabetes: a position statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(Suppl 1):S61–78. - PubMed
-
- Arkan MC, Hevener AL, Greten FR, Maeda S, Li ZW, Long JM, Wynshaw-Boris A, Poli G, Olefsky J, Karin M. IKK-beta links inflammation to obesity-induced insulin resistance. Nat Med. 2005;11:191–198. - PubMed
-
- Arner P. Catecholamine-induced lipolysis in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1999;23(Suppl 1):10–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 DK113065/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK089503/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002240/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000433/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK076906/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK100319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK098776/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK105075/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK060591/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

