Fibroblast deletion of ROCK2 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction
- PMID: 28679962
- PMCID: PMC5499369
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.93187
Fibroblast deletion of ROCK2 attenuates cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction
Abstract
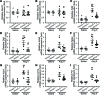
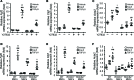
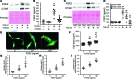
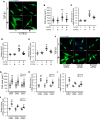
Although left ventricular (LV) diastolic dysfunction is often associated with hypertension, little is known regarding its underlying pathophysiological mechanism. Here, we show that the actin cytoskeletal regulator, Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinase-2 (ROCK2), is a critical mediator of LV diastolic dysfunction. In response to angiotensin II (Ang II), mutant mice with fibroblast-specific deletion of ROCK2 (ROCK2Postn-/-) developed less LV wall thickness and fibrosis, along with improved isovolumetric relaxation. This corresponded with decreased connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF2) expression in the hearts of ROCK2Postn-/- mice. Indeed, knockdown of ROCK2 in cardiac fibroblasts leads to decreased expression of CTGF and secretion of FGF2, and cardiomyocytes incubated with conditioned media from ROCK2-knockdown cardiac fibroblasts exhibited less hypertrophic response. In contrast, mutant mice with elevated fibroblast ROCK activity exhibited enhanced Ang II-stimulated cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Clinically, higher leukocyte ROCK2 activity was observed in patients with diastolic dysfunction compared with age- and sex-matched controls, and correlated with higher grades of diastolic dysfunction by echocardiography. These findings indicate that fibroblast ROCK2 is necessary to cause cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through the induction CTGF and FGF2, and they suggest that targeting ROCK2 may have therapeutic benefits in patients with LV diastolic dysfunction.
Keywords: Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
FHL2 prevents cardiac hypertrophy in mice with cardiac-specific deletion of ROCK2.FASEB J. 2013 Apr;27(4):1439-49. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-217018. Epub 2012 Dec 27. FASEB J. 2013. PMID: 23271052 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial Role of ROCK2-Mediated Phosphorylation and Upregulation of FHOD3 in the Pathogenesis of Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy.Hypertension. 2017 Jun;69(6):1070-1083. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08662. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28438902
-
Differential role of TIMP2 and TIMP3 in cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, and diastolic dysfunction.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Jul 15;103(2):268-80. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu072. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24692173
-
Connective tissue growth factor inhibition attenuates left ventricular remodeling and dysfunction in pressure overload-induced heart failure.Hypertension. 2014 Jun;63(6):1235-40. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03279. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24688123
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
IGF-1 protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by targeting αSMA.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 9;12(7):688. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03965-5. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34244467 Free PMC article.
-
Selectivity matters: selective ROCK2 inhibitor ameliorates established liver fibrosis via targeting inflammation, fibrosis, and metabolism.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 18;6(1):1176. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05552-0. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37980369 Free PMC article.
-
Statins change the cytokine profile in Trypanosoma cruzi-infected U937 macrophages and murine cardiac tissue through Rho-associated kinases inhibition.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 11;13:1035589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035589. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713380 Free PMC article.
-
The level of ROCK1 and ROCK2 in patients with pulmonary hypertension in plateau area.Sci Rep. 2018 Jun 19;8(1):9356. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-27321-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29921927 Free PMC article.
-
ROCK Inhibition as Potential Target for Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension.Cells. 2021 Jun 30;10(7):1648. doi: 10.3390/cells10071648. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34209333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

