Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Combination With Ipilimumab in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: The CheckMate 016 Study
- PMID: 28678668
- PMCID: PMC7587408
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.72.1985
Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab in Combination With Ipilimumab in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: The CheckMate 016 Study
Abstract
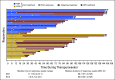
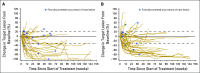
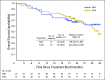
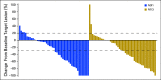
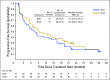
Purpose Combination treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors has shown enhanced antitumor activity compared with monotherapy in tumor types such as melanoma. The open-label, parallel-cohort, dose-escalation, phase I CheckMate 016 study evaluated the efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in combination, and nivolumab plus a tyrosine kinase inhibitor in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Safety and efficacy results from the nivolumab plus ipilimumab arms of the study are presented. Patients and Methods Patients with mRCC received intravenous nivolumab 3 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 1 mg/kg (N3I1), nivolumab 1 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 3 mg/kg (N1I3), or nivolumab 3 mg/kg plus ipilimumab 3 mg/kg (N3I3) every 3 weeks for four doses followed by nivolumab monotherapy 3 mg/kg every 2 weeks until progression or toxicity. End points included safety (primary), objective response rate, and overall survival (OS). Results All patients in the N3I3 arm (n = 6) were censored at the time of analysis as a result of dose-limiting toxicity or other reasons. Forty-seven patients were treated in both the N3I1 and the N1I3 arm, and baseline patient characteristics were balanced between arms. Grade 3 to 4 treatment-related adverse events were reported in 38.3% and 61.7% of the patients in the N3I1 and N1I3 arms, respectively. At a median follow-up of 22.3 months, the confirmed objective response rate was 40.4% in both arms, with ongoing responses in 42.1% and 36.8% of patients in the N3I1 and N1I3 arms, respectively. The 2-year OS was 67.3% and 69.6% in the N3I1 and N1I3 arms, respectively. Conclusion Nivolumab plus ipilimumab therapy demonstrated manageable safety, notable antitumor activity, and durable responses with promising OS in patients with mRCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2018 Apr 5;378(14):1277-1290. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1712126. Epub 2018 Mar 21. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 29562145 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up of efficacy and safety results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2019 Oct;20(10):1370-1385. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30413-9. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Lancet Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31427204 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with sunitinib or pazopanib in advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the CheckMate 016 study.J Immunother Cancer. 2018 Oct 22;6(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0420-0. J Immunother Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30348216 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy and safety of combined immune checkpoint inhibitors (nivolumab plus ipilimumab): a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Jul 3;18(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01933-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32620130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ipilimumab in combination with nivolumab for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018 Sep;18(9):947-957. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2018.1513485. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30124333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential.Cell. 2015 Apr 9;161(2):205-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.030. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25860605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clear-cell renal cell carcinoma - A comprehensive review of agents used in the contemporary management of advanced/metastatic disease.Oncol Rev. 2021 Feb 26;15(1):530. doi: 10.4081/oncol.2021.530. eCollection 2021 Feb 26. Oncol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33747368 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Key Prognostic Biomarker and Its Correlation with Immune Infiltrates in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2020 Aug 31;2020:8825997. doi: 10.1155/2020/8825997. eCollection 2020. Dis Markers. 2020. PMID: 32934754 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab in the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: clinical trial evidence and experience.Ther Adv Urol. 2016 Oct;8(5):319-326. doi: 10.1177/1756287216656811. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Ther Adv Urol. 2016. PMID: 27695530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relapse of aseptic meningitis induced by ipilimumab and nivolumab therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A case report.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec;11(6):590-594. doi: 10.3892/mco.2019.1929. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31700625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. : Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 136:E359-E386, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Gupta K, Miller JD, Li JZ, et al. : Epidemiologic and socioeconomic burden of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC): A literature review. Cancer Treat Rev 34:193-205, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

