The heterotrimeric G protein Gβ1 interacts with the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 and modulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling in platelets
- PMID: 28615442
- PMCID: PMC5555177
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.796656
The heterotrimeric G protein Gβ1 interacts with the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 and modulates G protein-coupled receptor signaling in platelets
Abstract
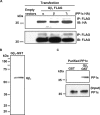
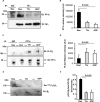
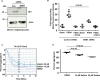
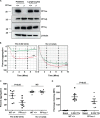
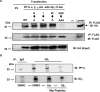
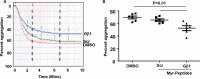
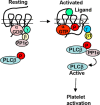
Thrombosis is caused by the activation of platelets at the site of ruptured atherosclerotic plaques. This activation involves engagement of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) on platelets that promote their aggregation. Although it is known that protein kinases and phosphatases modulate GPCR signaling, how serine/threonine phosphatases integrate with G protein signaling pathways is less understood. Because the subcellular localization and substrate specificity of the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1c) is dictated by PP1c-interacting proteins, here we sought to identify new PP1c interactors. GPCRs signal via the canonical heterotrimeric Gα and Gβγ subunits. Using a yeast two-hybrid screen, we discovered an interaction between PP1cα and the heterotrimeric G protein Gβ1 subunit. Co-immunoprecipitation studies with epitope-tagged PP1c and Gβ1 revealed that Gβ1 interacts with the PP1c α, β, and γ1 isoforms. Purified PP1c bound to recombinant Gβ1-GST protein, and PP1c co-immunoprecipitated with Gβ1 in unstimulated platelets. Thrombin stimulation of platelets induced the dissociation of the PP1c-Gβ1 complex, which correlated with an association of PP1c with phospholipase C β3 (PLCβ3), along with a concomitant dephosphorylation of the inhibitory Ser1105 residue in PLCβ3. siRNA-mediated depletion of GNB1 (encoding Gβ1) in murine megakaryocytes reduced protease-activated receptor 4, activating peptide-induced soluble fibrinogen binding. Thrombin-induced aggregation was decreased in PP1cα-/- murine platelets and in human platelets treated with a small-molecule inhibitor of Gβγ. Finally, disruption of PP1c-Gβ1 complexes with myristoylated Gβ1 peptides containing the PP1c binding site moderately decreased thrombin-induced human platelet aggregation. These findings suggest that Gβ1 protein enlists PP1c to modulate GPCR signaling in platelets.
Keywords: ADP; G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR); megakaryocytes; phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1); platelet; protein phosphatase 1; thrombin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
The catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 gamma regulates thrombin-induced murine platelet alpha(IIb)beta(3) function.PLoS One. 2009 Dec 15;4(12):e8304. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008304. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 20016849 Free PMC article.
-
Gbeta residues that do not interact with Galpha underlie agonist-independent activity of K+ channels.J Biol Chem. 2002 Mar 1;277(9):7348-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109999200. Epub 2001 Nov 13. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11707461
-
Opposing Roles for the α Isoform of the Catalytic Subunit of Protein Phosphatase 1 in Inside-Out and Outside-In Integrin Signaling in Murine Platelets.Cells. 2023 Oct 10;12(20):2424. doi: 10.3390/cells12202424. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887268 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin light chain phosphatase: subunit composition, interactions and regulation.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1998 May;19(4):325-41. doi: 10.1023/a:1005385302064. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1998. PMID: 9635276 Review.
-
Controlling Ser/Thr protein phosphatase PP1 activity and function through interaction with regulatory subunits.Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020;122:231-288. doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2020.06.004. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32951813 Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphenols in wound healing: unlocking prospects with clinical applications.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 25. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03538-1. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39453503
-
Cellular human tissue-engineered skin substitutes investigated for deep and difficult to heal injuries.NPJ Regen Med. 2021 Jun 17;6(1):35. doi: 10.1038/s41536-021-00144-0. NPJ Regen Med. 2021. PMID: 34140525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of G proteins and their GTPase-activating proteins in platelets.Biosci Rep. 2024 May 29;44(5):BSR20231420. doi: 10.1042/BSR20231420. Biosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38808367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymer-Based Wound Dressings Loaded with Ginsenoside Rg3.Molecules. 2023 Jun 28;28(13):5066. doi: 10.3390/molecules28135066. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37446725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase Cγ2 Signaling Cascade Contribute to the Antiplatelet Effect of Notoginsenoside Fc.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Nov 6;9:1293. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01293. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30459626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shankar H., Kahner B., and Kunapuli S. P. (2006) G-protein dependent platelet signaling–perspectives for therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 7, 1253–1263 - PubMed
-
- Ford C. E., Skiba N. P., Bae H., Daaka Y., Reuveny E., Shekter L. R., Rosal R., Weng G., Yang C. S., Iyengar R., Miller R. J., Jan L. Y., Lefkowitz R. J., and Hamm H. E. (1998) Molecular basis for interactions of G protein βγ subunits with effectors. Science 280, 1271–1274 - PubMed
-
- Ceulemans H., and Bollen M. (2004) Functional diversity of protein phosphatase-1, a cellular economizer and reset button. Physiol. Rev. 84, 1–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

