Identification of the elementary structural units of the DNA damage response
- PMID: 28604675
- PMCID: PMC5472794
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms15760
Identification of the elementary structural units of the DNA damage response
Abstract
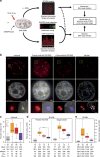
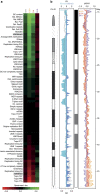
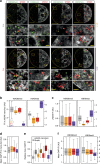
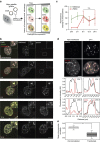
Histone H2AX phosphorylation is an early signalling event triggered by DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). To elucidate the elementary units of phospho-H2AX-labelled chromatin, we integrate super-resolution microscopy of phospho-H2AX during DNA repair in human cells with genome-wide sequencing analyses. Here we identify phospho-H2AX chromatin domains in the nanometre range with median length of ∼75 kb. Correlation analysis with over 60 genomic features shows a time-dependent euchromatin-to-heterochromatin repair trend. After X-ray or CRISPR-Cas9-mediated DSBs, phospho-H2AX-labelled heterochromatin exhibits DNA decondensation while retaining heterochromatic histone marks, indicating that chromatin structural and molecular determinants are uncoupled during repair. The phospho-H2AX nano-domains arrange into higher-order clustered structures of discontinuously phosphorylated chromatin, flanked by CTCF. CTCF knockdown impairs spreading of the phosphorylation throughout the 3D-looped nano-domains. Co-staining of phospho-H2AX with phospho-Ku70 and TUNEL reveals that clusters rather than nano-foci represent single DSBs. Hence, each chromatin loop is a nano-focus, whose clusters correspond to previously known phospho-H2AX foci.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Super-resolution localization microscopy of radiation-induced histone H2AX-phosphorylation in relation to H3K9-trimethylation in HeLa cells.Nanoscale. 2018 Mar 1;10(9):4320-4331. doi: 10.1039/c7nr08145f. Nanoscale. 2018. PMID: 29443341
-
gammaH2AX foci form preferentially in euchromatin after ionising-radiation.PLoS One. 2007 Oct 24;2(10):e1057. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001057. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17957241 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of elimination of phosphorylated histone H2AX from chromatin after repair of DNA double-strand breaks.Mutat Res. 2010 Mar 1;685(1-2):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.08.001. Epub 2009 Aug 12. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 19682466 Review.
-
H2AX chromatin structures and their response to DNA damage revealed by 4Pi microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 28;103(48):18137-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608709103. Epub 2006 Nov 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17110439 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Oct;36(17):5678-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn550. Epub 2008 Sep 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18772227 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Double-strand break repair and mis-repair in 3D.DNA Repair (Amst). 2023 Jan;121:103430. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103430. Epub 2022 Nov 17. DNA Repair (Amst). 2023. PMID: 36436496 Free PMC article.
-
DNA replication and repair kinetics of Alu, LINE-1 and satellite III genomic repetitive elements.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Oct 23;11(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0226-9. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 30352618 Free PMC article.
-
miR-4443 promotes radiation resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting PTPRJ.J Transl Med. 2022 Dec 28;20(1):626. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03818-5. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36578050 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Behavior of Chromatin in Response to DNA Double-Strand Breaks.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jan 25;13(2):215. doi: 10.3390/genes13020215. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA choreography: correlating mobility and organization of DNA across different resolutions from loops to chromosomes.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Jul;162(1-2):109-131. doi: 10.1007/s00418-024-02285-x. Epub 2024 May 17. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38758428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rogakou E. P., Pilch D. R., Orr A. H., Ivanova V. S. & Bonner W. M. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 5858–5868 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Stucki M. & Jackson S. P. GammaH2AX and MDC1: anchoring the DNA-damage-response machinery to broken chromosomes. DNA Repair 5, 534–543 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Bartkova J. et al.. DNA damage response as a candidate anti-cancer barrier in early human tumorigenesis. Nature 434, 864–870 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Gorgoulis V. G. et al.. Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature 434, 907–913 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

