Etiology of epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with type 2 inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 28583447
- PMCID: PMC5753806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.04.010
Etiology of epithelial barrier dysfunction in patients with type 2 inflammatory diseases
Abstract
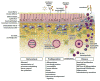
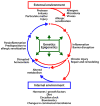
Epithelial barriers of the skin, gastrointestinal tract, and airway serve common critical functions, such as maintaining a physical barrier against environmental insults and allergens and providing a tissue interface balancing the communication between the internal and external environments. We now understand that in patients with allergic disease, regardless of tissue location, the homeostatic balance of the epithelial barrier is skewed toward loss of differentiation, reduced junctional integrity, and impaired innate defense. Importantly, epithelial dysfunction characterized by these traits appears to pre-date atopy and development of allergic disease. Despite our growing appreciation of the centrality of barrier dysfunction in initiation of allergic disease, many important questions remain to be answered regarding mechanisms disrupting normal barrier function. Although our external environment (proteases, allergens, and injury) is classically thought of as a principal contributor to barrier disruption associated with allergic sensitization, there is a need to better understand contributions of the internal environment (hormones, diet, and circadian clock). Systemic drivers of disease, such as alterations of the endocrine system, metabolism, and aberrant control of developmental signaling, are emerging as new players in driving epithelial dysfunction and allergic predisposition at various barrier sites. Identifying such central mediators of epithelial dysfunction using both systems biology tools and causality-driven laboratory experimentation will be essential in building new strategic interventions to prevent or reverse the process of barrier loss in allergic patients.
Keywords: Epithelial barrier; allergic predisposition; allergic sensitization; differentiation; extracellular matrix; hormones; mesenchyme; metabolism; tight junctions.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Barrier dysfunction caused by environmental proteases in the pathogenesis of allergic diseases.Allergol Int. 2011 Mar;60(1):25-35. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.10-RAI-0273. Epub 2011 Dec 25. Allergol Int. 2011. PMID: 21173566 Review.
-
Circadian Regulation of the Biology of Allergic Disease: Clock Disruption Can Promote Allergy.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 12;11:1237. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01237. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32595651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The epithelial barrier and immunoglobulin A system in allergy.Clin Exp Allergy. 2016 Nov;46(11):1372-1388. doi: 10.1111/cea.12830. Epub 2016 Oct 21. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016. PMID: 27684559 Review.
-
Epithelial barrier function: at the front line of asthma immunology and allergic airway inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Sep;134(3):509-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.05.049. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25085341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Skin barrier dysfunction and systemic sensitization to allergens through the skin.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005 Oct;4(5):531-41. doi: 10.2174/156801005774322199. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16248822 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae airways infection: the next treatable trait in asthma?Eur Respir Rev. 2022 Sep 20;31(165):220008. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0008-2022. Print 2022 Sep 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2022. PMID: 36130784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Reprogramming of Nasal Airway Epithelial Cells Following Infant Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection.Viruses. 2021 Oct 13;13(10):2055. doi: 10.3390/v13102055. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696488 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic Modulation of Type 2 Immune Responses.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 19;8:1873. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01873. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29312347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The long noncoding RNA Falcor regulates Foxa2 expression to maintain lung epithelial homeostasis and promote regeneration.Genes Dev. 2019 Jun 1;33(11-12):656-668. doi: 10.1101/gad.320523.118. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Genes Dev. 2019. PMID: 30923168 Free PMC article.
-
Budesonide repairs decreased barrier integrity of eosinophilic nasal polyp epithelial cells caused by PM2.5.Clin Transl Allergy. 2021 Jul 3;11(5):e12019. doi: 10.1002/clt2.12029. eCollection 2021 Jul. Clin Transl Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34262692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thyssen JP, Kezic S. Causes of epidermal filaggrin reduction and their role in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134:792–9. - PubMed
-
- Pellerin L, Henry J, Hsu CY, Balica S, Jean-Decoster C, Mechin MC, et al. Defects of filaggrin-like proteins in both lesional and nonlesional atopic skin. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013;131:1094–102. - PubMed
-
- Palmer CN, Irvine AD, Terron-Kwiatkowski A, Zhao Y, Liao H, Lee SP, et al. Common loss-of-function variants of the epidermal barrier protein filaggrin are a major predisposing factor for atopic dermatitis. Nat Genet. 2006;38:441–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

