Preparation of Purified Gram-positive Bacterial Cell Wall and Detection in Placenta and Fetal Tissues
- PMID: 28573167
- PMCID: PMC5448413
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2037
Preparation of Purified Gram-positive Bacterial Cell Wall and Detection in Placenta and Fetal Tissues
Abstract
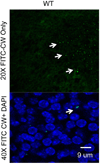
Cell wall is a complex biopolymer on the surface of all Gram-positive bacteria. During infection, cell wall is recognized by the innate immune receptor Toll-like receptor 2 causing intense inflammation and tissue damage. In animal models, cell wall traffics from the blood stream to many organs in the body, including brain, heart, placenta and fetus. This protocol describes how to prepare purified cell wall from Streptococcus pneumoniae, detect its distribution in animal tissues, and study the tissue response using the placenta and fetal brain as examples.
Keywords: Bacterial inflammation; Cell wall; Fetal neurogenesis; Neuroproliferation; Peptidoglycan; Placental trafficking; Streptococcus pneumonae; Toll like receptor 2 ligand.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cutting edge: recognition of Gram-positive bacterial cell wall components by the innate immune system occurs via Toll-like receptor 2.J Immunol. 1999 Jul 1;163(1):1-5. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10384090
-
Bacterial Peptidoglycan Traverses the Placenta to Induce Fetal Neuroproliferation and Aberrant Postnatal Behavior.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Mar 9;19(3):388-99. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.02.009. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 26962947 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with the Gram-positive bacterial cell wall molecule peptidoglycan improves bacterial clearance and decreases inflammation and mortality in mice challenged with Staphylococcus aureus.Crit Care Med. 2008 Nov;36(11):3067-73. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31818c6fb7. Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18824898 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory activity of cell-wall constituents from gram-positive bacteria.Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35(9):632-41. doi: 10.1080/00365540310016259. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 14620147 Review.
-
Lipoteichoic acids as a major virulence factor causing inflammatory responses via Toll-like receptor 2.Arch Pharm Res. 2016 Nov;39(11):1519-1529. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0804-y. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Arch Pharm Res. 2016. PMID: 27498542 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of Gram-negative Bacteria Peptidoglycan by Ultra-performance Liquid Chromatography.Bio Protoc. 2020 Oct 5;10(19):e3780. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3780. eCollection 2020 Oct 5. Bio Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33659436 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial peptidoglycan muropeptides benefit mitochondrial homeostasis and animal physiology by acting as ATP synthase agonists.Dev Cell. 2022 Feb 7;57(3):361-372.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2021.12.016. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Dev Cell. 2022. PMID: 35045336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun JS, Novak R, Herzoq KH, Bodmer SM, Cleveland JL, Tuomanen EI. Neuroprotection by a caspase inhibitor in acute bacterial meningitis. Nat Med. 1999;5:298–302. - PubMed
-
- Fillon S, Soulis K, Rajasekaran S, Benedict-Hamilton H, Radin JN, Orihuela CJ, Kasmi KC, Murti G, Kaushal D, Gaber MW, Weber JR, Murray PJ, Tuomanen EI. Platelet-activating factor receptor and innate immunity: uptake of gram-positive bacterial cell wall into host cells and cell-specific pathophysiology. J Immunol. 2006;177:6182–6191. - PubMed
-
- Holtje JV, Tomasz A. Specific recognition of choline residues in the cell wall teichoic acid by the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase of Pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1975;250(15):6072–6076. - PubMed
-
- Humann J, Mann B, Gao G, Moresco P, Ramahi J, Loh LN, Farr A, Hu Y, Durick Eder K, Fillon SA, Smeyne RJ, Tuomanen EI. Bacterial peptidoglycan traverses the placenta to induce fetal neuroproliferation and aberrant postnatal behavior. Cell Host Microbe. 2016;19(6):901. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

