Topographic analysis by atomic force microscopy of proteoliposomes matrix vesicle mimetics harboring TNAP and AnxA5
- PMID: 28549727
- PMCID: PMC5793902
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.05.010
Topographic analysis by atomic force microscopy of proteoliposomes matrix vesicle mimetics harboring TNAP and AnxA5
Abstract
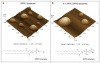
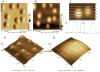
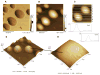
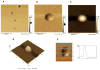
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is one of the most commonly used scanning probe microscopy techniques for nanoscale imaging and characterization of lipid-based particles. However, obtaining images of such particles using AFM is still a challenge. The present study extends the capabilities of AFM to the characterization of proteoliposomes, a special class of liposomes composed of lipids and proteins, mimicking matrix vesicles (MVs) involved in the biomineralization process. To this end, proteoliposomes were synthesized, composed of 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DPPC) and 1,2-dipalmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-l-serine (DPPS), with inserted tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP) and/or annexin V (AnxA5), both characteristic proteins of osteoblast-derived MVs. We then aimed to study how TNAP and AnxA5 insertion affects the proteoliposomes' membrane properties and, in turn, interactions with type II collagen, thus mimicking early MV activity during biomineralization. AFM images of these proteoliposomes, acquired in dynamic mode, revealed the presence of surface protrusions with distinct viscoelasticity, thus suggesting that the presence of the proteins induced local changes in membrane fluidity. Surface protrusions were measurable in TNAP-proteoliposomes but barely detectable in AnxA5-proteoliposomes. More complex surface structures were observed for proteoliposomes harboring both TNAP and AnxA5 concomitantly, resulting in a lower affinity for type II collagen fibers compared to proteoliposomes harboring AnxA5 alone. The present study achieved the topographic analysis of lipid vesicles by direct visualization of structural changes, resulting from protein incorporation, without the need for fluorescent probes.
Keywords: Annexin V; Atomic force microscopy; Collagen; Matrix vesicles; Proteoliposomes; Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrix vesicle biomimetics harboring Annexin A5 and alkaline phosphatase bind to the native collagen matrix produced by mineralizing vascular smooth muscle cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020 Aug;1864(8):129629. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2020.129629. Epub 2020 Apr 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2020. PMID: 32360152 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoliposomes with the ability to transport Ca(2+) into the vesicles and hydrolyze phosphosubstrates on their surface.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015 Oct 15;584:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2015.08.018. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2015. PMID: 26325078 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoliposomes harboring alkaline phosphatase and nucleotide pyrophosphatase as matrix vesicle biomimetics.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 5;285(10):7598-609. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.079830. Epub 2010 Jan 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20048161 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix vesicles from chondrocytes and osteoblasts: Their biogenesis, properties, functions and biomimetic models.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 Mar;1862(3):532-546. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29108957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of phosphatases in the initiation of skeletal mineralization.Calcif Tissue Int. 2013 Oct;93(4):299-306. doi: 10.1007/s00223-012-9672-8. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Calcif Tissue Int. 2013. PMID: 23183786 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research and application of hydrostatic high pressure in tumor vaccines (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 May;45(5):75. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8026. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33760193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix vesicles from dental follicle cells improve alveolar bone regeneration via activation of the PLC/PKC/MAPK pathway.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jan 29;13(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02721-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35093186 Free PMC article.
-
Langmuir monolayers and proteoliposomes as models of matrix vesicles involved in biomineralization.Biophys Rev. 2021 Nov 10;13(6):893-895. doi: 10.1007/s12551-021-00866-x. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biophys Rev. 2021. PMID: 35059014 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Chloroform-Injection (CI) and Spontaneous-Phase-Transition (SPT) Are Novel Methods, Simplifying the Fabrication of Liposomes with Versatile Solution to Cholesterol Content and Size Distribution.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Nov 9;12(11):1065. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12111065. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 33182248 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylserine controls calcium phosphate nucleation and growth on lipid monolayers: A physicochemical understanding of matrix vesicle-driven biomineralization.J Struct Biol. 2020 Nov 1;212(2):107607. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2020.107607. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 32858148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolean M, Simao AM, Favarin BZ, Millan JL, Ciancaglini P. The effect of cholesterol on the reconstitution of alkaline phosphatase into liposomes. Biophys Chem. 2010;152:74–79. - PubMed
-
- Wuthier RE. Lipids of matrix vesicles. Fed Proc. 1976;35:117–121. - PubMed
-
- Anderson HC. Mineralization by matrix vesicles Scan. Electron Microsc. 1984:953–964. - PubMed
-
- Thouverey C, Strzelecka-Kiliszek A, Balcerzak M, Buchet R, Pikula S. Matrix vesicles originate from apical membrane microvilli of mineralizing osteoblast-like Saos-2 cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106:127–138. - PubMed
-
- Wuthier RE, Lipscomb GF. Matrix vesicles: structure, composition, formation and function in calcification. Front Biosci. 2011;16:2812–2902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

