MicroRNA-146a reduces MHC-II expression via targeting JAK/STAT signaling in dendritic cells after stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 28484267
- PMCID: PMC6231537
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.137
MicroRNA-146a reduces MHC-II expression via targeting JAK/STAT signaling in dendritic cells after stem cell transplantation
Abstract
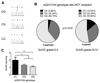
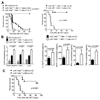
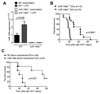
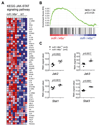
Acute Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a major immunological complication after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation and a better understanding of the molecular regulation of the disease could help to develop novel targeted therapies. Here we found that a G/C polymorphism within the human microRNA-146a (miR-146a) gene of transplant recipients, which causes reduced miR-146a levels, was strongly associated with the risk of developing severe acute GVHD (n=289). In mice, deficiency of miR-146a in the hematopoietic system or transfer of recipient-type miR-146a-/- dendritic cells (DCs) enhanced GVHD, while miR-146a mimic-transfected DCs ameliorated disease. Mechanistically, lack of miR-146a enhanced JAK2-STAT1 pathway activity, which led to higher expression of class II-transactivator (CIITA) and consecutively increased MHCII-levels on DCs. Inhibition of JAK1/2 or CIITA knockdown in DCs prevented miR-146a-/- DC-induced GVHD exacerbation. Consistent with our findings in mice, patients with the miR-146a polymorphism rs2910164 in hematopoietic cells displayed higher MHCII levels on monocytes, which could be targeted by JAK1/2 inhibition. Our findings indicate that the miR-146a polymorphism rs2910164 identifies patients at high risk for GVHD before allo-HCT. Functionally we show that miR-146a acts as a central regulator of recipient-type DC activation during GVHD by dampening the pro-inflammatory JAK-STAT/CIITA/MHCII axis, which provides a scientific rationale for early JAK1/2 inhibition in selected patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-146a regulates the TRAF6/TNF-axis in donor T cells during GVHD.Blood. 2014 Oct 16;124(16):2586-95. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-569046. Epub 2014 Sep 9. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25205119
-
MicroRNA-155-deficient dendritic cells cause less severe GVHD through reduced migration and defective inflammasome activation.Blood. 2015 Jul 2;126(1):103-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-12-617258. Epub 2015 May 13. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25972159
-
miR-146a down-regulation alleviates H2O2-induced cytotoxicity of PC12 cells by regulating MCL1/JAK/STAT pathway : miR-146a down-regulation relieves H2O2-induced PC12 cells cytotoxicity by MCL1/JAK/STAT.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2018 Dec;34(6):479-489. doi: 10.1007/s10565-018-9424-2. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29484526
-
The Role of Janus Kinase Signaling in Graft-Versus-Host Disease and Graft Versus Leukemia.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018 Jun;24(6):1125-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.12.797. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. PMID: 29289756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Janus Kinase Inhibitors and Cell Therapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 31;12:740847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.740847. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34531878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination of TLR agonist and miR146a mimics attenuates ovalbumin-induced asthma.Mol Med. 2020 Jun 29;26(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s10020-020-00191-1. Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32600285 Free PMC article.
-
miR-146a Controls Immune Response in the Melanoma Microenvironment.Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 1;79(1):183-195. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1397. Epub 2018 Nov 13. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30425059 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-17-92 is required for T-cell and B-cell pathogenicity in chronic graft-versus-host disease in mice.Blood. 2018 Apr 26;131(17):1974-1986. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-789321. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29530952 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin alpha-V is an important driver in pancreatic adenocarcinoma progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 26;40(1):214. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01946-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34174926 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-cancer analysis of oncogenic TNFAIP2 identifying its prognostic value and immunological function in acute myeloid leukemia.BMC Cancer. 2022 Oct 15;22(1):1068. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10155-9. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36243694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson A, Schelter JM, Castle J, et al. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 2005 Feb 17;433(7027):769–773. - PubMed
-
- Stickel N, Prinz G, Pfeifer D, Hasselblatt P, Schmitt-Graeff A, Follo M, et al. MiR-146a regulates the TRAF6/TNF-axis in donor T cells during GVHD. Blood. 2014 Oct 16;124(16):2586–2595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

