Association of Endothelial Glycocalyx and Tight and Adherens Junctions With Severity of Plasma Leakage in Dengue Infection
- PMID: 28453844
- PMCID: PMC5407050
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix041
Association of Endothelial Glycocalyx and Tight and Adherens Junctions With Severity of Plasma Leakage in Dengue Infection
Abstract
Background: The role of vascular endothelial (VE) components in dengue infection with plasma leakage is unknown. Therefore, we conducted a study to determine the adjusted association of the endothelial glycocalyx layer (EGL) and tight and adherens junction markers with plasma leakage.
Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted at Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital and Persahabatan Hospital, Jakarta, Indonesia. Adult dengue patients admitted to the hospital on the third day of fever from November 2013 through August 2015 were included in the study. Multiple regression analysis was used to determine the adjusted association of the VE biomarkers with the severity of the plasma leakage.
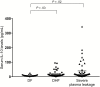
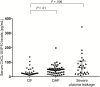
Results: A total of 103 dengue-infected patients participated in the study. In the critical phase, levels of syndecan-1 (odds ratio [OR] = 1.004; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.001-1.007) and chondroitin sulfate (OR = 1.157; 95% CI = 1.025-1.307) had an adjusted association with plasma leakage, whereas levels of syndecan-1 (OR = 1.004; 95% CI = 1.000-1.008) and claudin-5 (OR = 1.038; 95% CI = 1.004-1.074) had an adjusted association with severe plasma leakage.
Conclusions: In dengue-infected patients, elevated levels of syndecan-1 and chondroitin sulfate are strongly associated with plasma leakage, and elevated levels of syndecan-1 and claudin-5 are strongly associated with severe plasma leakage.
Keywords: chondroitin sulfate; claudin-5; dengue infection; plasma leakage; syndecan-1.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated Plasma Concentrations of Syndecan-1 Do Not Correlate With Increased Capillary Leakage of 20% Albumin.Anesth Analg. 2021 Mar 1;132(3):856-865. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005315. Anesth Analg. 2021. PMID: 33350618 Clinical Trial.
-
Increased Plasma Heparanase Activity and Endothelial Glycocalyx Degradation in Dengue Patients Is Associated With Plasma Leakage.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 20;12:759570. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.759570. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987504 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial glycocalyx shedding and vascular permeability in severely injured trauma patients.J Transl Med. 2015 Apr 12;13:117. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0481-5. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889764 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Glycocalyx as Biomarker for Cardiovascular Diseases: Mechanistic and Clinical Implications.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017 Apr;14(2):117-126. doi: 10.1007/s11897-017-0320-5. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017. PMID: 28233259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human glycocalyx shedding: Systematic review and critical appraisal.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021 May;65(5):590-606. doi: 10.1111/aas.13797. Epub 2021 Mar 7. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021. PMID: 33595101 Review.
Cited by
-
The association between obesity and dengue virus (DENV) infection in hospitalised patients.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 17;13(7):e0200698. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200698. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30016369 Free PMC article.
-
Increased serum sialic acid is associated with morbidity and mortality in a murine model of dengue disease.J Gen Virol. 2019 Nov;100(11):1515-1522. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001319. J Gen Virol. 2019. PMID: 31526452 Free PMC article.
-
Raised Serum Levels of Syndecan-1 (CD138), in a Case of Acute Idiopathic Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome (SCLS) (Clarkson's Disease).Am J Case Rep. 2018 Feb 16;19:176-182. doi: 10.12659/ajcr.906514. Am J Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29449526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dengue Virus Induces the Expression and Release of Endocan from Endothelial Cells by an NS1-TLR4-Dependent Mechanism.Microorganisms. 2021 Jun 15;9(6):1305. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9061305. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34203931 Free PMC article.
-
The Glycocalyx and Its Role in Vascular Physiology and Vascular Related Diseases.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021 Feb;12(1):37-71. doi: 10.1007/s13239-020-00485-9. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2021. PMID: 32959164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srikiatkhachorn A, Krautrachue A, Ratanaprakarn W, et al. Natural history of plasma leakage in dengue hemorrhagic fever: a serial ultrasonographic study. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2007; 26:283–90; discussion 91–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

