KCa1.1 channels regulate β1-integrin function and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- PMID: 28428266
- PMCID: PMC5503717
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201601097R
KCa1.1 channels regulate β1-integrin function and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Abstract
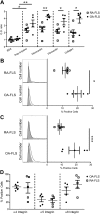
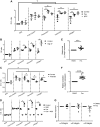
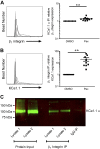
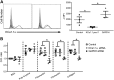
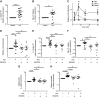
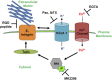
Large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (KCa1.1; BK, Slo1, MaxiK, KCNMA1) is the predominant potassium channel expressed at the plasma membrane of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes (RA-FLSs) isolated from the synovium of patients with RA. It is a critical regulator of RA-FLS migration and invasion and therefore represents an attractive target for the therapy of RA. However, the molecular mechanisms by which KCa1.1 regulates RA-FLS invasiveness have remained largely unknown. Here, we demonstrate that KCa1.1 regulates RA-FLS adhesion through controlling the plasma membrane expression and activation of β1 integrins, but not α4, α5, or α6 integrins. Blocking KCa1.1 disturbs calcium homeostasis, leading to the sustained phosphorylation of Akt and the recruitment of talin to β1 integrins. Interestingly, the pore-forming α subunit of KCa1.1 coimmunoprecipitates with β1 integrins, suggesting that this physical association underlies the functional interaction between these molecules. Together, these data outline a new signaling mechanism by which KCa1.1 regulates β1-integrin function and therefore invasiveness of RA-FLSs.-Tanner, M. R., Pennington, M. W., Laragione, T., Gulko, P. S., Beeton, C. KCa1.1 channels regulate β1-integrin function and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Keywords: invasion; migration; synovial fibroblast.
© FASEB.
Figures

Similar articles
-
KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channels regulate the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T lymphocytes during rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jan 7;21(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1783-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30612588 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the therapeutic opportunities of potassium channels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1286069. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1286069. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different expression of β subunits of the KCa1.1 channel by invasive and non-invasive human fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 May 10;18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1003-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27165430 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting KCa1.1 Channels with a Scorpion Venom Peptide for the Therapy of Rat Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 May;365(2):227-236. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.245118. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 29453198 Free PMC article.
-
An emerging spectrum of variants and clinical features in KCNMA1-linked channelopathy.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):447-464. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1938852. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 34224328 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KCa1.1 and Kv1.3 channels regulate the interactions between fibroblast-like synoviocytes and T lymphocytes during rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jan 7;21(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1783-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30612588 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function of artesunate on inhibiting migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Jun 24;21(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1935-6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31234900 Free PMC article.
-
pH-Channeling in Cancer: How pH-Dependence of Cation Channels Shapes Cancer Pathophysiology.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 2;12(9):2484. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092484. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32887220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the therapeutic opportunities of potassium channels for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 9;15:1286069. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1286069. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38783950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in ion channel phenotype and function between humans and animal models.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018 Jan 1;23(1):43-64. doi: 10.2741/4581. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2018. PMID: 28930537 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hynes R. O. (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110, 673–687 - PubMed
-
- Hood J. D., Cheresh D. A. (2002) Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 91–100 - PubMed
-
- Levite M., Cahalon L., Peretz A., Hershkoviz R., Sobko A., Ariel A., Desai R., Attali B., Lider O. (2000) Extracellular K(+) and opening of voltage-gated potassium channels activate T cell integrin function: physical and functional association between Kv1.3 channels and beta1 integrins. J. Exp. Med. 191, 1167–1176 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matheu M. P., Beeton C., Garcia A., Chi V., Rangaraju S., Safrina O., Monaghan K., Uemura M. I., Li D., Pal S., de la Maza L. M., Monuki E., Flügel A., Pennington M. W., Parker I., Chandy K. G., Cahalan M. D. (2008) Imaging of effector memory T cells during a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction and suppression by Kv1.3 channel block. Immunity 29, 602–614 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

