Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 28426781
- PMCID: PMC5398705
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176071
Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
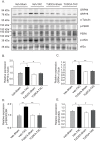
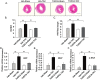
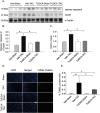
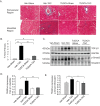
Pressure overload in the heart induces pathological hypertrophy and is associated with cardiac dysfunction. Apoptosis and fibrosis signaling initiated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) is known to contribute to these maladaptive effects. The aim of this study was to investigate whether reduction of ERS by a known chemical chaperone, tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) can attenuate pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling in a mouse model of transverse aortic constriction (TAC). Oral administration of TUDCA at a dose of 300 mg/kg body weight (BW) in the TUDCA-TAC group reduced ERS markers (GRP78, p-PERK, and p-eIf2α), compared to the Vehicle (Veh)-TAC group. TUDCA administration, for 4 weeks after TAC significantly reduced cardiac hypertrophy as shown by the reduced heart weight (HW) to BW ratio, and expression of hypertrophic marker genes (ANF, BNP, and α-SKA). Masson's trichrome staining showed that myocardial fibrosis and collagen deposition were also significantly reduced in the TUDCA-TAC group. We also found that TUDCA significantly decreased expression of TGF-β signaling proteins and collagen isoforms. TUDCA administration also reduced cardiac apoptosis and the related proteins in the TUDCA-TAC group. Microarray analysis followed by gene ontology (GO) and pathway analysis demonstrated that extracellular matrix genes responsible for hypertrophy and fibrosis, and mitochondrial genes responsible for apoptosis and fatty acid metabolism were significantly altered in the Veh-TAC group, but the alterations were normalized in the TUDCA-TAC group, suggesting potential of TUDCA in treatment of heart diseases related to pressure-overload.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyric acid attenuates pressure-overload cardiac hypertrophy by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012 May 11;421(3):578-84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.048. Epub 2012 Apr 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012. PMID: 22525677
-
4-PBA prevents pressure overload-induced myocardial hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress.Chem Biol Interact. 2015 Dec 5;242:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.09.025. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Chem Biol Interact. 2015. PMID: 26428355 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Uremic Cardiomyopathy: Protective Effects of Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(1):141-52. doi: 10.1159/000438616. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 26765262
-
Tauroursodeoxycholate-Bile Acid with Chaperoning Activity: Molecular and Cellular Effects and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cells. 2019 Nov 20;8(12):1471. doi: 10.3390/cells8121471. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31757001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The bile acid TUDCA and neurodegenerative disorders: An overview.Life Sci. 2021 May 1;272:119252. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119252. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33636170 Review.
Cited by
-
Update in Interstitial Lung Disease 2019.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Aug 15;202(4):500-507. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202002-0360UP. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32412784 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Rescue of HSP70 in Spinal Neurons Alleviates Opioids-Induced Hyperalgesia via the Suppression of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Rodents.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 May 12;8:269. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00269. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32500072 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac proteostasis in obesity and cardiovascular disease.Herz. 2024 Mar;49(2):118-123. doi: 10.1007/s00059-024-05233-6. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Herz. 2024. PMID: 38329532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disruption of Enterohepatic Circulation of Bile Acids Ameliorates Small Bowel Resection Associated Hepatic Injury.J Pediatr Surg. 2023 Jun;58(6):1074-1078. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2023.02.031. Epub 2023 Feb 21. J Pediatr Surg. 2023. PMID: 36914459 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in pulmonary fibrosis.Matrix Biol. 2018 Aug;68-69:355-365. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2018.03.015. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Matrix Biol. 2018. PMID: 29567124 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frey N, Katus HA, Olson EN, Hill JA. Hypertrophy of the heart a new therapeutic target? Circulation. 2004;109:1580–1589. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000120390.68287.BB - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yoshida H. ER stress and diseases. FEBS J. 2007;274:630–658. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2007.05639.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kaufman RJ. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1211–1233. - PubMed
-
- Groenendyk J, Sreenivasaiah PK, Kim DH, Agellon LB, Michalak M. Biology of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the heart. Circ Res. 2010;107:1185–1197. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.227033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Minamino T, Komuro I, Kitakaze M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2010;107:1071–1082. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.227819 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

