Prevention of Chronic Hepatitis B after 3 Decades of Escalating Vaccination Policy, China
- PMID: 28418296
- PMCID: PMC5403029
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2305.161477
Prevention of Chronic Hepatitis B after 3 Decades of Escalating Vaccination Policy, China
Abstract
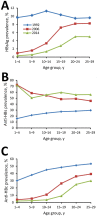
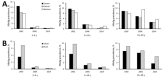
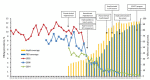
China's hepatitis B virus (HBV) prevention policy has been evaluated through nationally representative serologic surveys conducted in 1992 and 2006. We report results of a 2014 serologic survey and reanalysis of the 1992 and 2006 surveys in the context of program policy. The 2014 survey used a 2-stage sample strategy in which townships were selected from 160 longstanding, nationally representative, county-level disease surveillance points, and persons 1-29 years of age were invited to participate. The 2014 sample size was 31,713; the response rate was 83.3%. Compared with the 1992 pre-recombinant vaccine survey, HBV surface antigen prevalence declined 46% by 2006 and by 52% by 2014. Among children <5 years of age, the decline was 97%. China's HBV prevention program, targeted toward interrupting perinatal transmission, has been highly successful and increasingly effective. However, this progress must be sustained for decades to come, and elimination of HBV transmission will require augmented strategies.
Keywords: China; hepatitis B; immunization; vaccination; vaccine; viruses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A mathematical model of hepatitis B virus transmission and its application for vaccination strategy in china.Int J Epidemiol. 2000 Aug;29(4):744-52. doi: 10.1093/ije/29.4.744. Int J Epidemiol. 2000. PMID: 10922354
-
Progress in hepatitis B prevention through universal infant vaccination--China, 1997-2006.MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007 May 11;56(18):441-5. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007. PMID: 17495790
-
Elimination of new chronic hepatitis B virus infections: results of the Alaska immunization program.J Infect Dis. 2000 Feb;181(2):413-8. doi: 10.1086/315259. J Infect Dis. 2000. PMID: 10669320
-
Impact of the implementation of a vaccination strategy on hepatitis B virus infections in China over a 20-year period.Int J Infect Dis. 2012 Feb;16(2):e82-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.10.009. Epub 2011 Dec 17. Int J Infect Dis. 2012. PMID: 22178658 Review.
-
Nationwide hepatitis B vaccination program in Taiwan: effectiveness in the 20 years after it was launched.Epidemiol Rev. 2006;28:126-35. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxj010. Epub 2006 Jun 16. Epidemiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16782778 Review.
Cited by
-
Survey of Hepatitis B Vaccination Coverage and Surface Antibody-Positive Rates in People Aged 1-59 Years in 2006 and 2024.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024 Oct 5;11(10):ofae589. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofae589. eCollection 2024 Oct. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39431151 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse event reporting following immunization of hepatitis B vaccine: A 13-year review.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2411824. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2411824. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39396824 Free PMC article.
-
Factors predicting the level of vaccine protection against hepatitis B virus infection among physicians and nurses in Šabac, Serbia.Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024 Sep 29;75(3):191-199. doi: 10.2478/aiht-2024-75-3828. eCollection 2024 Sep 1. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2024. PMID: 39369330 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of gastrointestinal cancers among working-age population over past thirty years in China.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):3955-3979. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i9.3955. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39350983 Free PMC article.
-
New progress in HBV control and the cascade of health care for people living with HBV in China: evidence from the fourth national serological survey, 2020.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024 Sep 14;51:101193. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101193. eCollection 2024 Oct. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2024. PMID: 39315090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis B [cited 2015 Nov 16]. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs204/en
-
- Li Y. Epidemiology of virus hepatitis in China. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology. 1986;Suppl (Viral Hepatitis):1–14.
-
- Dai Z, Qi G. Virus hepatitis in China: seroepidemiological survey in Chinese population (part one) 1992–1995. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Literature Press; 1996. p. 8–103.
-
- Qu Z. Epidemiological study on the distribution of HBsAg and anti-HBs in China. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology. 1986;Suppl (Viral Hepatitis):20–40.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

