Rare Genetic Variants in PARN Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis in Families
- PMID: 28414520
- PMCID: PMC5736978
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201703-0635LE
Rare Genetic Variants in PARN Are Associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis in Families
Figures
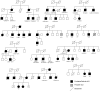
Similar articles
-
Pulmonary fibrosis in the era of stratified medicine.Thorax. 2016 Dec;71(12):1154-1160. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-209172. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Thorax. 2016. PMID: 27799632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Exome Sequencing Study to Assess the Role of Rare Genetic Variation in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017 Jul 1;196(1):82-93. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201610-2088OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 28099038 Free PMC article.
-
Homozygous Rare PARN Missense Mutation in Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Mar 15;199(6):797-799. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201809-1632LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30525901 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetic susceptibility and pulmonary fibrosis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2014 Sep;20(5):429-35. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000074. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2014. PMID: 25022318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic inheritance of telomere length obscures identification of causative PARN locus.J Med Genet. 2016 May;53(5):356-8. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103685. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 26908837 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Progress in Understanding and Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Annu Rev Med. 2019 Jan 27;70:211-224. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-041317-102715. Annu Rev Med. 2019. PMID: 30691371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics and Genomics of Pulmonary Fibrosis: Charting the Molecular Landscape and Shaping Precision Medicine.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024 Aug 15;210(4):401-423. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202401-0238SO. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2024. PMID: 38573068 Review.
-
Peripheral Blood Telomere Attrition in Persons at Risk for Familial Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023 Jan 15;207(2):208-211. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202204-0766LE. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36036734 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Analysis of protein-altering variants in telomerase genes and their association with MUC5B common variant status in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a candidate gene sequencing study.Lancet Respir Med. 2018 Aug;6(8):603-614. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(18)30135-8. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Lancet Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 29891356 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular markers of telomere dysfunction and senescence are common findings in the usual interstitial pneumonia pattern of lung fibrosis.Histopathology. 2021 Jul;79(1):67-76. doi: 10.1111/his.14334. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Histopathology. 2021. PMID: 33432658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burris AM, Ballew BJ, Kentosh JB, Turner CE, Norton SA, Giri N, Alter BP, Nellan A, Gamper C, Hartman KR, et al. NCI DCEG Cancer Genomics Research Laboratory; NCI DCEG Cancer Sequencing Working Group. Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome due to PARN mutations: fourteen years of follow-up. Pediatr Neurol. 2016;56:62–68. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dhanraj S, Gunja SM, Deveau AP, Nissbeck M, Boonyawat B, Coombs AJ, Renieri A, Mucciolo M, Marozza A, Buoni S, et al. Bone marrow failure and developmental delay caused by mutations in poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN) J Med Genet. 2015;52:738–748. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

