Anthracyclines in Early Breast Cancer: The ABC Trials-USOR 06-090, NSABP B-46-I/USOR 07132, and NSABP B-49 (NRG Oncology)
- PMID: 28398846
- PMCID: PMC5549453
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.71.4147
Anthracyclines in Early Breast Cancer: The ABC Trials-USOR 06-090, NSABP B-46-I/USOR 07132, and NSABP B-49 (NRG Oncology)
Abstract
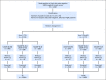
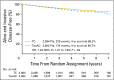
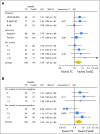
Purpose Docetaxel and cyclophosphamide (TC) was superior to doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide (AC) in a trial in early breast cancer. However, activity of TC relative to AC regimens with a taxane (TaxAC) is unknown. Methods In a series of three adjuvant trials, women were randomly assigned to TC for six cycles (TC6) or to a standard TaxAC regimen. US Oncology Research (USOR) 06-090 compared TC6 with docetaxel, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide (TAC6). National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) B-46-I/USOR 07132 compared TC6, TAC6, or TC6 plus bevacizumab. NSABP B-49 compared TC6 with several standard AC and taxane combination regimens. Before any analysis of individual trials, a joint efficacy analysis of TC versus the TaxAC regimens was planned, with invasive disease-free survival (IDFS) as the primary end point. Patients who received TC6 plus bevacizumab on NSABP B-46-I/USOR 07132 were not included. A hazard ratio (HR) from a stratified Cox model that exceeded 1.18 for TC6 versus TaxAC was predefined as inferiority for TC6. The prespecified interim monitoring plan was to report for futility if the HR was > 1.18 when 334 IDFS events were observed (50% of 668 events required for definitive analysis). Results A total of 2,125 patients were randomly assigned to receive TC6 regimens and 2,117 patients were randomly assigned to receive TaxAC regimens. The median follow-up time was 3.3 years. There were 334 IDFS events, and the HR for TC6 versus TaxAC was 1.202 (95% CI, 0.97 to 1.49), which triggered early reporting for futility. The 4-year IDFS was 88.2% for TC6 and was 90.7% for TaxAC ( P = .04). Tests for treatment interaction by protocol, hormone receptor status, and nodal status were negative. Conclusion The TaxAC regimens improved IDFS in patients with high-risk human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer compared with the TC6 regimen.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Follow-Up of the Anthracyclines in Early Breast Cancer Trials (USOR 06-090, NSABP B-46-I/USOR 07132, and NSABP B-49 [NRG Oncology]).J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 20;42(12):1344-1349. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.01428. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38335467
-
Comparison of an AC-taxane versus AC-free regimen and paclitaxel versus docetaxel in patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer: Final results of the National Surgical Adjuvant Study of Breast Cancer 02 trial, a randomized comparative phase 3 study.Cancer. 2017 Mar 1;123(5):759-768. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30421. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28081304 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adjuvant bevacizumab-containing therapy in triple-negative breast cancer (BEATRICE): primary results of a randomised, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2013 Sep;14(10):933-42. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70335-8. Epub 2013 Aug 7. Lancet Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23932548 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of an Adjuvant Chemotherapy Regimen for Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.JAMA Oncol. 2015 Dec;1(9):1311-8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2015.3062. JAMA Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26402167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maximizing the Clinical Benefit of Anthracyclines in Addition to Taxanes in the Adjuvant Treatment of Early Breast Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Aug 10;35(23):2600-2603. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.5960. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28661760 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Follow-Up of the Anthracyclines in Early Breast Cancer Trials (USOR 06-090, NSABP B-46-I/USOR 07132, and NSABP B-49 [NRG Oncology]).J Clin Oncol. 2024 Apr 20;42(12):1344-1349. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.01428. Epub 2024 Feb 9. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38335467
-
The Comparative Safety of Epirubicin and Cyclophosphamide versus Docetaxel and Cyclophosphamide in Lymph Node-Negative, HR-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer (ELEGANT): A Randomized Trial.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 30;14(13):3221. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133221. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804991 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of adjuvant trastuzumab-containing chemotherapies for patients with early HER2-positive primary breast cancer: a network meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan;173(1):1-9. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4969-6. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30242579 Free PMC article.
-
CSCO breast cancer management guidelines 2022: Australian perspective.Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 31;3:36. doi: 10.21037/tbcr-22-46. eCollection 2022. Transl Breast Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 38751522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Outcomes of Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Chemotherapy, Biologic Therapy, Endocrine Therapy, or Active Surveillance During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Oncologist. 2022 Mar 4;27(2):89-96. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyab042. Oncologist. 2022. PMID: 35641208 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fisher B, Fisher ER, Redmond C: Ten-year results from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) clinical trial evaluating the use of L-phenylalanine mustard (L-PAM) in the management of primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 4:929-941, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bonadonna G, Valagussa P, Moliterni A, et al. : Adjuvant cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in node-positive breast cancer: The results of 20 years of follow-up. N Engl J Med 332:901-906, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, et al. : Improved outcomes from adding sequential paclitaxel but not from escalating doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 21:976-983, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Mamounas EP, Bryant J, Lembersky B, et al. : Paclitaxel after doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as adjuvant chemotherapy for node-positive breast cancer: Results from NSABP B-28. J Clin Oncol 23:3686-3696, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

