MSFragger: ultrafast and comprehensive peptide identification in mass spectrometry-based proteomics
- PMID: 28394336
- PMCID: PMC5409104
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4256
MSFragger: ultrafast and comprehensive peptide identification in mass spectrometry-based proteomics
Abstract
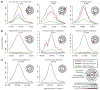
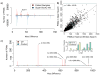
There is a need to better understand and handle the 'dark matter' of proteomics-the vast diversity of post-translational and chemical modifications that are unaccounted in a typical mass spectrometry-based analysis and thus remain unidentified. We present a fragment-ion indexing method, and its implementation in peptide identification tool MSFragger, that enables a more than 100-fold improvement in speed over most existing proteome database search tools. Using several large proteomic data sets, we demonstrate how MSFragger empowers the open database search concept for comprehensive identification of peptides and all their modified forms, uncovering dramatic differences in modification rates across experimental samples and conditions. We further illustrate its utility using protein-RNA cross-linked peptide data and using affinity purification experiments where we observe, on average, a 300% increase in the number of identified spectra for enriched proteins. We also discuss the benefits of open searching for improved false discovery rate estimation in proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


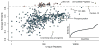
Similar articles
-
Fast Open Modification Spectral Library Searching through Approximate Nearest Neighbor Indexing.J Proteome Res. 2018 Oct 5;17(10):3463-3474. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00359. Epub 2018 Sep 13. J Proteome Res. 2018. PMID: 30184435 Free PMC article.
-
Fast Quantitative Analysis of timsTOF PASEF Data with MSFragger and IonQuant.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020 Sep;19(9):1575-1585. doi: 10.1074/mcp.TIR120.002048. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 32616513 Free PMC article.
-
VEMS 3.0: algorithms and computational tools for tandem mass spectrometry based identification of post-translational modifications in proteins.J Proteome Res. 2005 Nov-Dec;4(6):2338-47. doi: 10.1021/pr050264q. J Proteome Res. 2005. PMID: 16335983
-
A face in the crowd: recognizing peptides through database search.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011 Nov;10(11):R111.009522. doi: 10.1074/mcp.R111.009522. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 21876205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tandem Mass Spectrum Sequencing: An Alternative to Database Search Engines in Shotgun Proteomics.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;919:217-226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-41448-5_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27975219 Review.
Cited by
-
AI-Assisted Processing Pipeline to Boost Protein Isoform Detection.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2836:157-181. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4007-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38995541
-
OVOL2 sustains postnatal thymic epithelial cell identity.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 27;14(1):7786. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43456-z. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38012144 Free PMC article.
-
Protein degradation by human 20S proteasomes elucidates the interplay between peptide hydrolysis and splicing.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 7;15(1):1147. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45339-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38326304 Free PMC article.
-
Web of venom: exploration of big data resources in animal toxin research.Gigascience. 2024 Jan 2;13:giae054. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giae054. Gigascience. 2024. PMID: 39250076 Free PMC article.
-
Study on Tissue Homogenization Buffer Composition for Brain Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 2;10(10):2466. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102466. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289728 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skinner OS, Kelleher NL. Illuminating the dark matter of shotgun proteomics. Nat Biotech. 2015;33:717–718. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

