Lanatoside C, a cardiac glycoside, acts through protein kinase Cδ to cause apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 28387249
- PMCID: PMC5384006
- DOI: 10.1038/srep46134
Lanatoside C, a cardiac glycoside, acts through protein kinase Cδ to cause apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
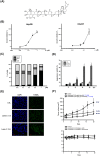
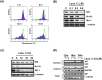
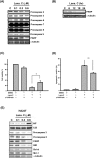
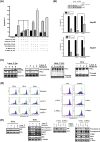
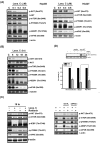
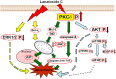
Recent studies have revealed that cardiac glycosides, such as digitalis and digoxin, have anticancer activity and may serve as lead compounds for the development of cancer treatments. The poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients reflects the development of resistance to current chemotherapeutic agents, highlighting the need for discovering new small-molecule therapeutics. Here, we found that lanatoside C, an anti-arrhythmic agent extracted from Digitalis lanata, inhibited the growth of HCC cells and dramatically decreased tumor volume as well as delayed tumor growth without obvious body weight loss. Moreover, lanatoside C triggered mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) loss, activation of caspases and translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) into the nucleus, which suggests that lanatoside C induced apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Furthermore, we discovered that lanatoside C activated protein kinase delta (PKCδ) via Thr505 phosphorylation and subsequent membrane translocation. Inhibition of PKCδ reversed lanatoside C-induced MMP loss and apoptosis, confirming that lanatoside C caused apoptosis through PKCδ activation. We also found that the AKT/mTOR pathway was negatively regulated by lanatoside C through PKCδ activation. In conclusion, we provide the first demonstration that the anticancer effects of lanatoside C are mainly attributable to PKCδ activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liver cancer cells are sensitive to Lanatoside C induced cell death independent of their PTEN status.Phytomedicine. 2016 Jan 15;23(1):42-51. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2015.11.012. Epub 2015 Dec 12. Phytomedicine. 2016. PMID: 26902406
-
Sprengerinin C exerts anti-tumorigenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibition of proliferation and angiogenesis and induction of apoptosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Aug 15;714(1-3):261-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 May 15. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23684542
-
Cardiac glycoside sensitized hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL via ROS generation, p38MAPK, mitochondrial transition, and autophagy mediation.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Nov;58(11):2040-2051. doi: 10.1002/mc.23096. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 31392779
-
Multiple subcellular localizations and functions of protein kinase Cδ in liver cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 14;28(2):188-198. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i2.188. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35110944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of protein kinase C-delta in DNA damage-induced apoptosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2003 Oct-Dec;7(4):341-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2003.tb00237.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2003. PMID: 14754503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer and Antiviral Properties of Cardiac Glycosides: A Review to Explore the Mechanism of Actions.Molecules. 2020 Aug 7;25(16):3596. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163596. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32784680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual targets of lethal apoptosis and protective autophagy in liver cancer with periplocymarin elicit a limited therapeutic effect.Int J Oncol. 2023 Mar;62(3):44. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5492. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36825592 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of Cardiac Glycosides as Potential Drugs: Current and Future Scope for Cancer Therapeutics.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 25;11(9):1275. doi: 10.3390/biom11091275. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34572488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lanatoside C Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest and Suppresses Cancer Cell Growth by Attenuating MAPK, Wnt, JAK-STAT, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathways.Biomolecules. 2019 Nov 27;9(12):792. doi: 10.3390/biom9120792. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31783627 Free PMC article.
-
Strophanthidin Induces Apoptosis of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells by Promoting TRAIL-DR5 Signaling.Molecules. 2024 Feb 16;29(4):877. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040877. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398629 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

