Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications
- PMID: 28386594
- PMCID: PMC5364456
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.6b00371
Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications
Abstract
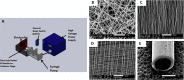
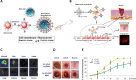
The chronic nature and associated complications of nonhealing wounds have led to the emergence of nanotechnology-based therapies that aim at facilitating the healing process and ultimately repairing the injured tissue. A number of engineered nanotechnologies have been proposed demonstrating unique properties and multiple functions that address specific problems associated with wound repair mechanisms. In this outlook, we highlight the most recently developed nanotechnology-based therapeutic agents and assess the viability and efficacy of each treatment, with emphasis on chronic cutaneous wounds. Herein we explore the unmet needs and future directions of current technologies, while discussing promising strategies that can advance the wound-healing field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Recent perspectives of nanotechnology in burn wounds management: a review.J Wound Care. 2021 May 2;30(5):350-370. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2021.30.5.350. J Wound Care. 2021. PMID: 33979218
-
Nanotechnology Approaches in Chronic Wound Healing.Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021 May;10(5):234-256. doi: 10.1089/wound.2019.1094. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021. PMID: 32320364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in inorganic nanomaterials for wound-healing applications.Biomater Sci. 2019 Jul 1;7(7):2652-2674. doi: 10.1039/c9bm00423h. Epub 2019 May 16. Biomater Sci. 2019. PMID: 31094374 Review.
-
Tissue Engineered Skin and Wound Healing: Current Strategies and Future Directions.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(24):3455-3482. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170526094606. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28552069 Review.
-
Advances of Stem Cell Therapeutics in Cutaneous Wound Healing and Regeneration.Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5217967. doi: 10.1155/2017/5217967. Epub 2017 Oct 29. Mediators Inflamm. 2017. PMID: 29213192 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutic Approach for Diabetic Wound Healing.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jun 25;10(6):1234. doi: 10.3390/nano10061234. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32630377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Towards Tunable Protein-Carrier Wound Dressings Based on Nanocellulose Hydrogels Crosslinked with Calcium Ions.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018 Jul 20;8(7):550. doi: 10.3390/nano8070550. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30036970 Free PMC article.
-
Alloyed nanostructures integrated metal-phenolic nanoplatform for synergistic wound disinfection and revascularization.Bioact Mater. 2022 Mar 19;16:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.03.004. eCollection 2022 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2022. PMID: 35386317 Free PMC article.
-
Dendrimer-Functionalized Metal Oxide Nanoparticle-Mediated Self-Assembled Collagen Scaffold for Skin Regenerative Application: Function of Metal in Metal Oxides.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;194(1):266-290. doi: 10.1007/s12010-021-03764-w. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 34817807
-
Recent Advances in Honey-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing: A Review.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 26;12(15):2560. doi: 10.3390/nano12152560. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35893528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

