TRAIL delivery by MSC-derived extracellular vesicles is an effective anticancer therapy
- PMID: 28326166
- PMCID: PMC5328331
- DOI: 10.1080/20013078.2017.1265291
TRAIL delivery by MSC-derived extracellular vesicles is an effective anticancer therapy
Abstract
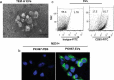
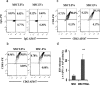
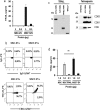
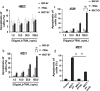
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are lipid membrane-enclosed nanoparticles released by cells. They mediate intercellular communication by transferring biological molecules and therefore have potential as innovative drug delivery vehicles. TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) selectively induces apoptosis of cancer cells. Unfortunately, the clinical application of recombinant rTRAIL has been hampered by its low bioavailability and resistance of cancer cells. EV-mediated TRAIL delivery may circumvent these problems. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) produce EVs and could be a good source for therapeutic EV production. We investigated if TRAIL could be expressed in MSC-derived EVs and examined their cancer cell-killing efficacy. EVs were isolated by ultracentrifugation and were membranous particles of 50-70 nm in diameter. Both MSC- and TRAIL-expressing MSC (MSCT)-derived EVs express CD63, CD9 and CD81, but only MSCT-EVs express surface TRAIL. MSCT-EVs induced apoptosis in 11 cancer cell lines in a dose-dependent manner but showed no cytotoxicity in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Caspase activity inhibition or TRAIL neutralisation blocked the cytotoxicity of TRAIL-positive EVs. MSCT-EVs induced pronounced apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant cancer cells and this effect could be further enhanced using a CDK9 inhibitor. These data indicate that TRAIL delivery by MSC-derived EVs is an effective anticancer therapy.
Keywords: EV; MSC; TRAIL; cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antitumor Activity of Cabazitaxel and MSC-TRAIL Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Drug-Resistant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Oct 29;12:10809-10820. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S277324. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33149686 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stromal cell delivery of full-length tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand is superior to soluble type for cancer therapy.Cytotherapy. 2015 Jul;17(7):885-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2015.03.603. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Cytotherapy. 2015. PMID: 25888191 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle Delivery of TRAIL Eradicates Resistant Tumor Growth in Combination with CDK Inhibition by Dinaciclib.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 4;12(5):1157. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051157. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32375399 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 10;15(5):1453. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051453. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineered Mesenchymal-Stromal-Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as an Improved Drug Delivery System: Methods and Applications.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 21;11(4):1231. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041231. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine and cancer; overview of development, challenges, and opportunities.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 May 21;12(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02378-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34020704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: A New Era in the Cell-Based Targeted Gene Therapy of Cancer.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 18;8:1770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01770. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29326689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical applications for exosomes: Are we there yet?Br J Pharmacol. 2021 Jun;178(12):2375-2392. doi: 10.1111/bph.15432. Epub 2021 May 3. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33751579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancement of therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Sep 23;10(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1398-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31547882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Delivery Modalities.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 2;15(2):504. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020504. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stenqvist A-C, Nagaeva O, Baranov V, et al. Exosomes secreted by human placenta carry functional Fas ligand and TRAIL molecules and convey apoptosis in activated immune cells, suggesting exosome-mediated immune privilege of the fetus. J Immunol. 2013;191(11):5515–5523. pii:jimmunol.1301885 DOI:10.4049/jimmunol.1301885 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

